Pain
At-Home Treatments for Osteoporosis

What is osteoporosis?
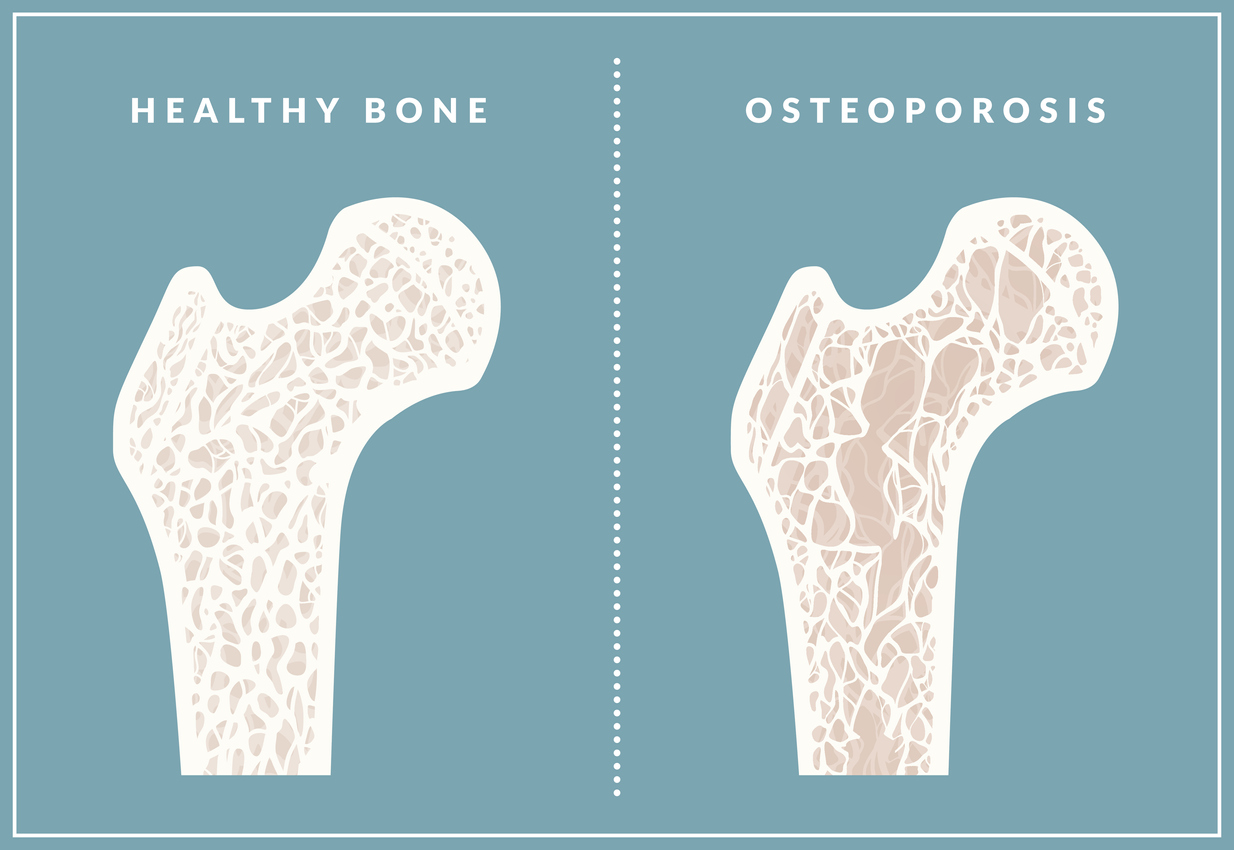
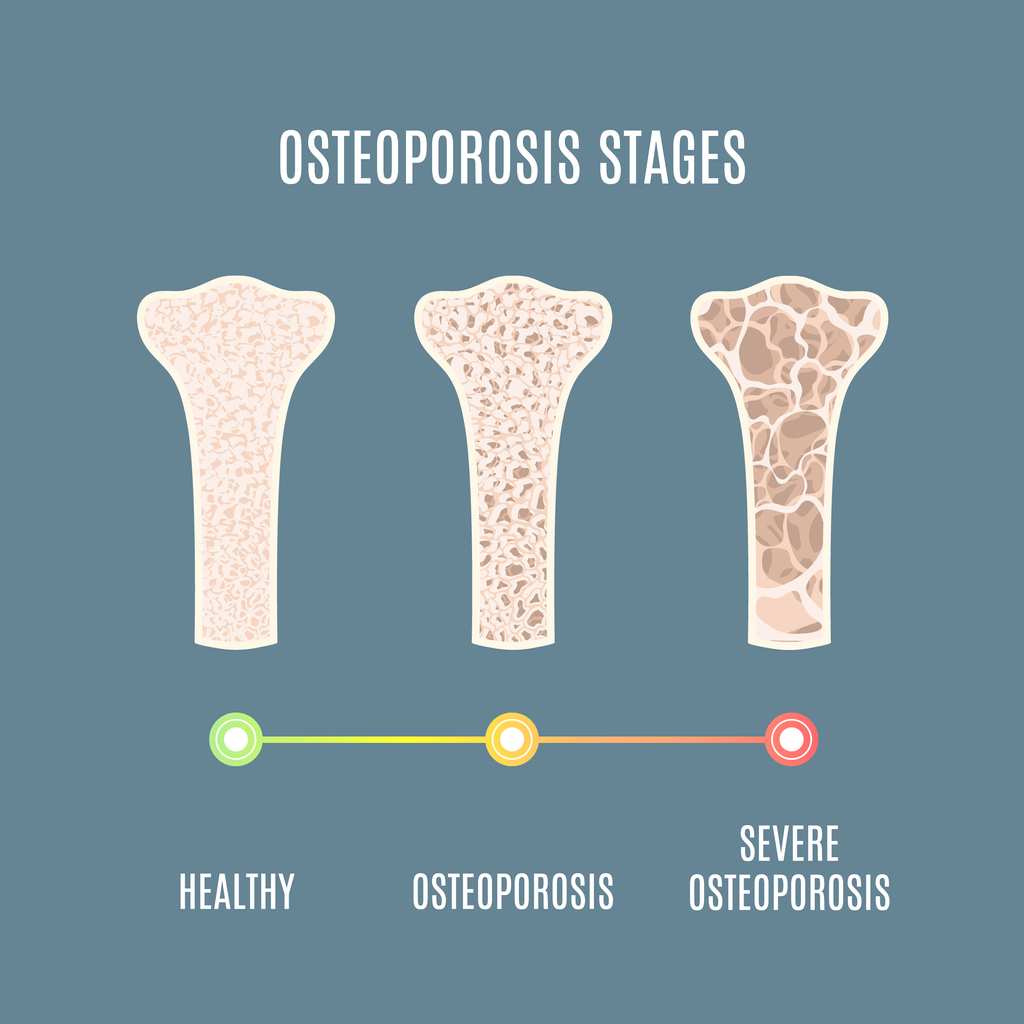
Osteoporosis is a condition that causes porous bones. The inside of a bone resembles a honeycomb. Osteoporosis causes this “honeycomb” spacing to increase, resulting in lost strength and density. The outside of the bones become brittle and weak.
This risk of fractures and breaks is increased with osteoporosis. An activity as simple as walking can cause a bone to fracture. In severe cases of osteoporosis, bones may become so brittle that a break can occur simply from coughing or bending the body. The bones most commonly affected by osteoporosis include the ribs, hips, wrists and spine.
At-home treatments
In addition to conventional treatment and alternative treatment for osteoporosis, certain at-home treatments options may help. They include, but are not limited to, engaging in physical activity, improved nutrition, limiting alcohol and caffeine, reducing fall risks, and stopping smoking.
Physical activity
Weight-bearing physical activity can help to increase bone density. This could include activities such as walking, running, or weightlifting. It is recommended to do these types of activities for 30-45 minutes at least three times per week.
Nutrition
Obtaining the appropriate amounts of both calcium and vitamin D is vital in the treatment of osteoporosis. Calcium helps build bone density; however, it is not absorbed without appropriate amounts of vitamin D.
- Calcium
Depending on age, between 1,000 and 1,200 mg of calcium is recommended daily. Good sources of calcium include nonfat milk, plant-based milk, fortified orange juice, low-fat yogurt, broccoli, tofu, salmon, cauliflower, and leafy green vegetables, such as spinach. Calcium is also available in supplements. - Vitamin D
Depending on age, 600 to 800 international units (IU) of vitamin D is recommended daily. This can be found in fortified milk or cereal and in certain fatty fish, including sardines, mackerel and salmon. Sunlight is the main source of vitamin D. Sunscreen can decrease the body’s vitamin D production; however, it is important in preventing skin cancer. Vitamin D can also be taken as a supplement. - Phosphorus
Too much phosphorus can promote bone loss. Foods that have high levels of phosphorus and should be limited include soft drinks, red meat, and foods with phosphate food additives.
Limit alcohol and caffeine
Alcohol and caffeine can both decrease the rate of calcium absorption in the body; therefore, intake should be limited. Drinking more than two alcoholic drinks per day has the potential to decrease bone formation and increase the risk of falling.
Stop smoking
Smoking cigarettes impairs blood flow, which causes less oxygen and nutrients to be delivered to vital organs, bones, tissues and muscles. Smoking tends to decrease bone mineral density, resulting in a higher risk of a fracture.
Prevent falls
Shoes should be low-heeled with a nonslip sole. Move cords and area rugs from the home to help prevent falls. Avoid any slippery surface and keep rooms lit brightly. Grab bars should be used when showering, and a bed rail is helpful when getting in and out of bed.