Pain
Information About Back Pain
An estimated eight out of every ten people will experience back pain at some point in their lives. Back pain is one of the most common reasons people visit a physician. It can be caused by normal wear and tear, overuse, injuries, muscles, bones, nerves, or discs. The most common causes of back pain are muscular irritation and joint dysfunction.
The spine
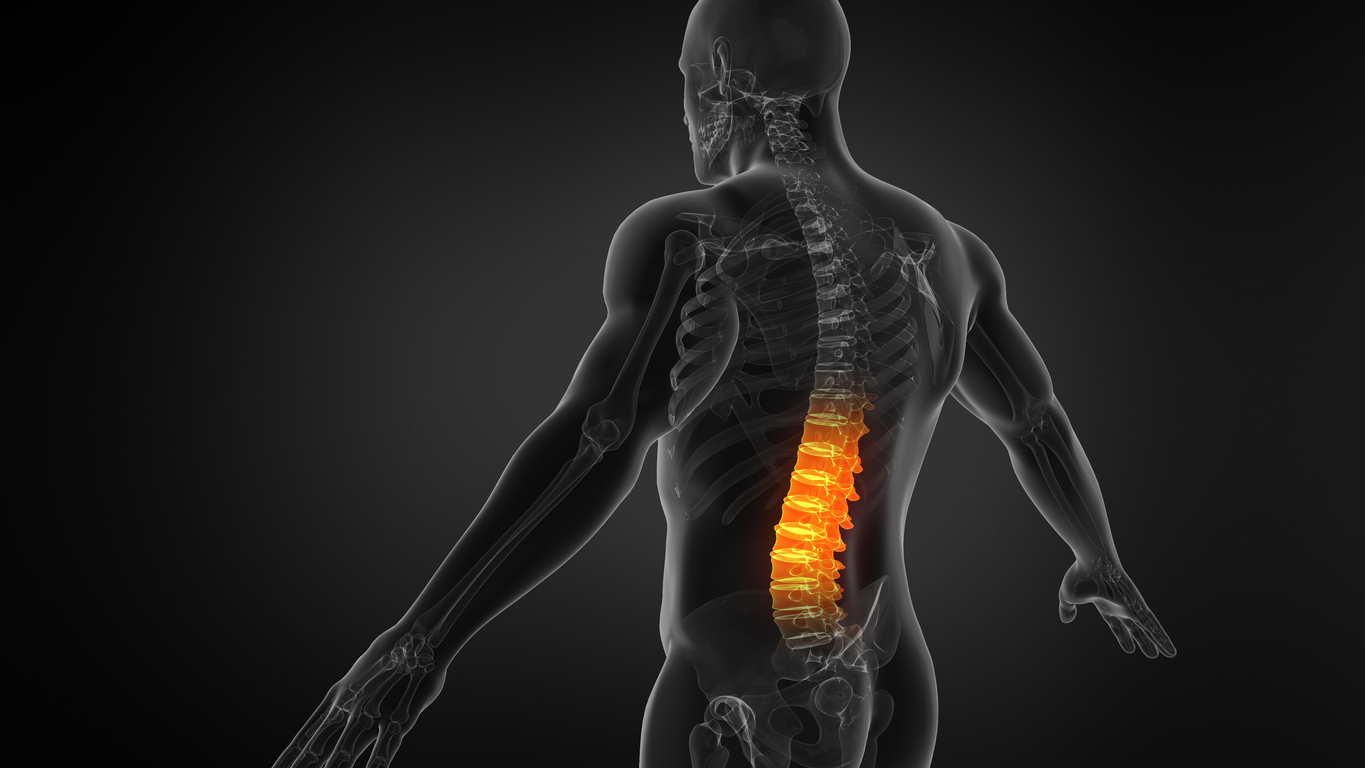
The spine, or backbone, runs from the neck to the lower back, close to the buttocks. The bones of the spine (vertebrae) form the spinal canal, which houses the spinal cord and nerves. The spine provides flexibility that allows a person to walk, twist, stand, bend and sit.
Although a person is normally born with 33 vertebrae, certain ones at the bottom of the spine fuse together during growth. Therefore, the spine of an average adult consists of 24 vertebrae (bones) that connect with facet joints. Discs are jelly-like cushions separating the bones of the spine (vertebrae). Ligaments stabilize the spine.
The sacrum is the bottom of the spine. The cervical spine (neck) has seven bones, the thoracic spine (chest) has 12 bones, and the lumbar spine (lower back) has five bones. The spinal column is composed of the vertebrae, ligaments, tendons, muscles, facet joints, and discs.
Common causes of back pain
Back pain can result from a variety of illnesses or accidents. The 10 most common causes of back pain include the following:
- Muscle or ligament strain
- Herniated disc
- Arthritis
- Degenerative disc disease
- Spinal stenosis
- Fracture
- Deformity
- Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS)
- Gallbladder issues
- Fibromyalgia
Diagnosing back pain
In order to receive appropriate treatment, a health care professional will need to make a correct diagnosis. Diagnostic tools can include the following:
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- Blood or urine test
- X-ray
- CT scan (computer tomography)
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging scan)
- Electromyogram (EMG)
- Bone scan
Treating back pain
The treatment of back pain is dependent on the cause. Treatment options include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), over-the-counter or prescription
- Chiropractic care
- Transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation (TENS)
- Bioelectric therapy
- Nerve blocks
- Spinal cord stimulator (SCS)
- Physical therapy
- Biofeedback
- Back surgery, as a last option