Pain
Lyme Disease Myths
Source: Healthline, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Biotechnology Information: U.S. National Library of Medicine: National Institutes of Health

7 people found this helpful
Print
Share
Save
What is Lyme disease?
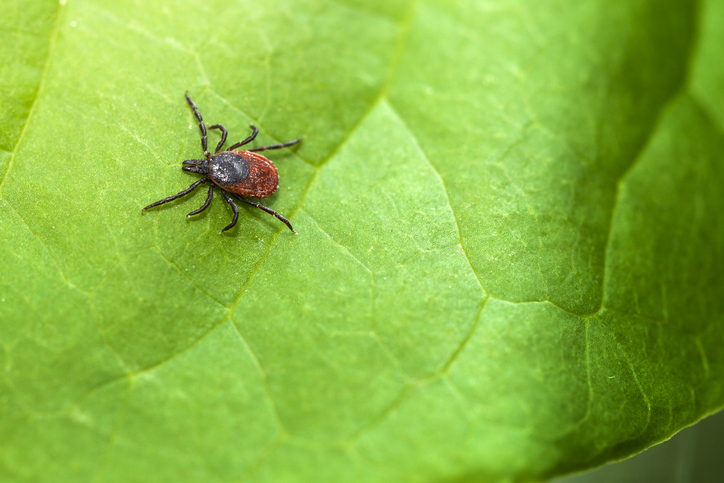
Lyme disease, or Lyme borreliosis, is an infectious disease caused by the bacteria Borrelia. The bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi and Borrelia mayonii are responsible for Lyme disease in North America. In Europe and Asia, Borrelia afzelii and Borrelia garinii are responsible for Lyme disease. The bacteria is spread to humans via the bite of an infected tick, usually a black-legged tick (commonly known as a deer tick).
Lyme disease myths
- Lyme disease only develops in individuals who remember a tick bite.
False: Less than 30% of individuals diagnosed with Lyme disease in the United States recall a tick bite. - Lyme disease is very rare.
False: Each year, 30,000 cases of Lyme disease are reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) by state health departments (including the District of Columbia) in the U.S. Unfortunately, this number does not reflect every case of Lyme disease diagnosed each year; in fact, estimates indicate that the number of people in the U.S. that may develop Lyme disease is closer to 300,000 annually. - A person who has Lyme disease can spread it to other people.
False: No evidence exists that Lyme disease is transmitted from person-to- person contact. - If a “bull’s-eye” rash does not develop, Lyme disease is not a possibility.
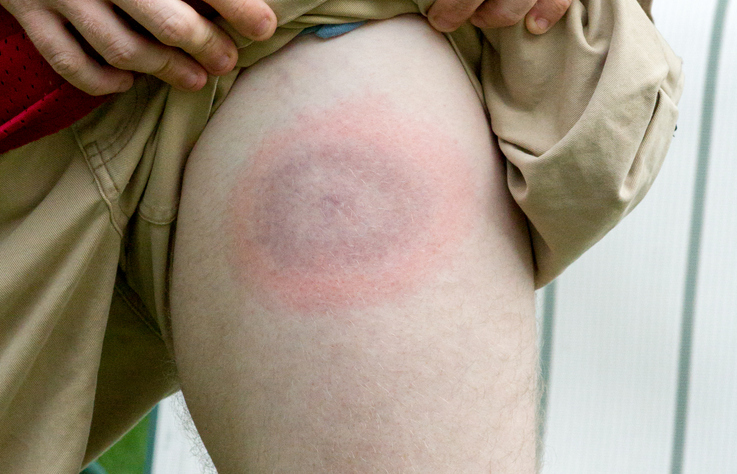
False: In some cases, the rash associated with Lyme disease, erythema migrans, does not have a “bull’s-eye” appearance, and many individuals who are diagnosed with Lyme disease do not recall a rash. - There is a vaccine for Lyme disease.
False: No vaccine is available for Lyme disease at this time. - Lyme disease transmission only occurs during warm seasons.
False: Infected ticks can transmit Lyme disease during any time of the year. - Lyme disease is an issue only in rural areas.
False: Infected ticks can transmit Lyme disease in both rural and urban areas.