Treatments
What Is an Epidural Injection?
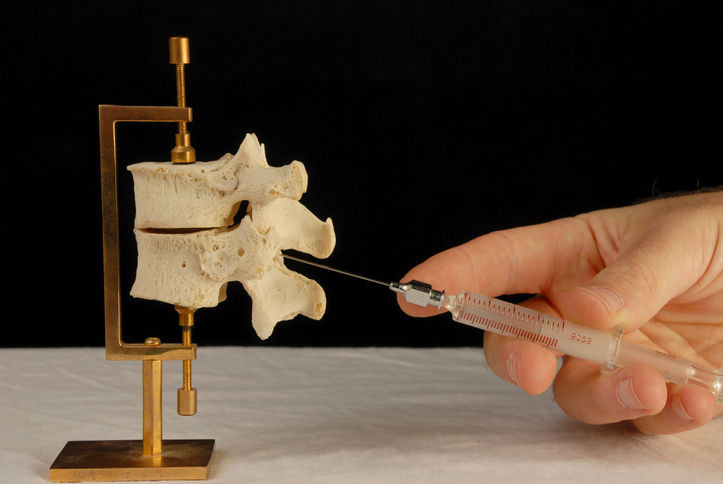
What is an epidural injection?
Epidural injections consist of delivery of medicine into the epidural space via a syringe. The epidural space is the fat-filled area covering the spinal cord. It protects the spinal cord and surrounding nerves from damage. Many people confuse an epidural anesthesia injection, widely known to relieve pain as women are giving birth, with an epidural steroid injection.
Epidural injections can help manage chronic pain and relieve pain during and after surgery. They can provide long-lasting pain relief with few side effects. Diagnostic epidurals can help with identifying underlying causes of pain.
The procedure
Epidural injections are normally outpatient procedures. Individuals are either lying face down, on their side, or sitting up. The injection site is sterilized and numbed. A needle with the steroid and numbing medication is inserted into the back, using x-rays to guide the needle. Contrast dye ensures the medicine goes to the direct area. Medicine injected into the affected area can decrease swelling and relieve nerve pain. Pressure may be felt during the injection; however, it is typically not painful. Individuals are monitored for 15 to 20 minutes before going home.
Numbing prior to the injection usually begins to work quickly. The epidural injection will take approximately 15 minutes. The steroid component of the injection should begin to ease pain in two to five days. If successful, benefits can last up to a few months, and the procedure can be repeated three to six times per year.
What conditions can epidural injections help?
Pain relief from an epidural injection may be short-term or experienced for several months. Epidural injections can provide pain relief for the following:
- Herniated disc
- Surgeries
- Pinched nerves
- Bone spurs
- Joint cysts
- Neck pain
- Back pain
- Pain from the spine
- Spinal stenosis
- Slipped vertebrae
- Spinal arthritis
Potential side effects of an epidural injection
Epidural steroid injections are generally safe. Side effects may include the following:
- Flushing
- Dizziness or headache
- Difficulty sleeping
- Water retention
- Anxiety
- Menstrual changes
- Increased pain for several days, which is rare
Rare but serious complications may include the following:
- Allergic reaction
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Nerve damage
- Paralysis
When to avoid epidural injections
A health care professional may want to delay or avoid epidural injections. Conditions that could make epidural injections risky include the following:
- Blood clotting issues
- Current infection
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Anesthesia drug allergies
- Certain medications