Treatments
What Is Erythema Ab Igne?
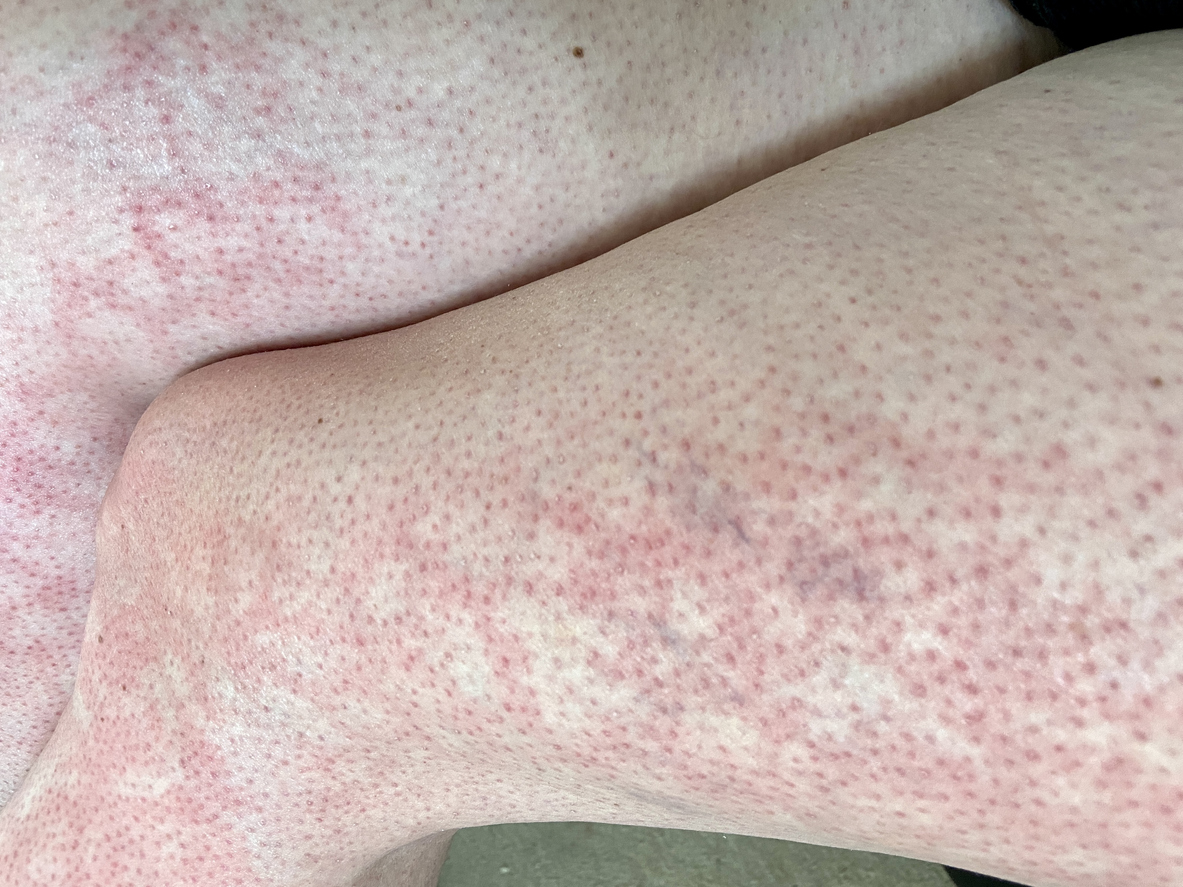
Erythema ab igne, or “toasted skin syndrome,” is a rare condition characterized by a localized rash (typically in a fishnet-type pattern), itch, burning sensation, and skin discoloration. This condition is the result of prolonged exposure to low-grade heat that is not hot enough to actually burn the skin. Caution should be used when treating chronic pain with heat.
On rare occasions, erythema ab igne may develop into cancer. A health care professional should monitor it closely for any changes that could be indicative of cancerous growth.
Symptoms
The main characteristic of erythema ab igne is skin discoloration. Typically, a red, brown, blue, or purple colored fishnet-type pattern will appear. Other symptoms include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Itching
- Burning
- Stinging
Causes
It is theorized that the elastic fibers of the skin, and blood vessels that sit closer to the skin’s surface, experience changes due to low heat (109.4-116.6 degrees Fahrenheit or 43-47 degrees Celsius) or infrared radiation exposure over long periods. Extended use of heating objects and activities that could lead to erythema ab igne include the following:
- Space heaters
- Heating pads or hot water bottles
- Heated seats in a vehicle
- Consistently placing a laptop on the thighs
- Electric stoves
- Electric blankets
- Open fires
- Hot baths
- Hot bricks
- Infrared lamps
Risk factors
Risk factors of developing erythema ab igne include the following:
- Children, due to greater skin sensitivity
- Adults aged 40-70
- Individuals with chronic pain in the lumbosacral region that use heat as to relieve pain
- Females