Pain
What Is Small Fiber Neuropathy?

Small fiber neuropathy (SFN) is a type of peripheral neuropathy. SFN is a nerve disorder characterized by unusual sensations, such as pain, burning, or tingling, that typically affect the feet. As time progresses, SNF can move upward through the body and, in later stages, may ultimately reach the hands.
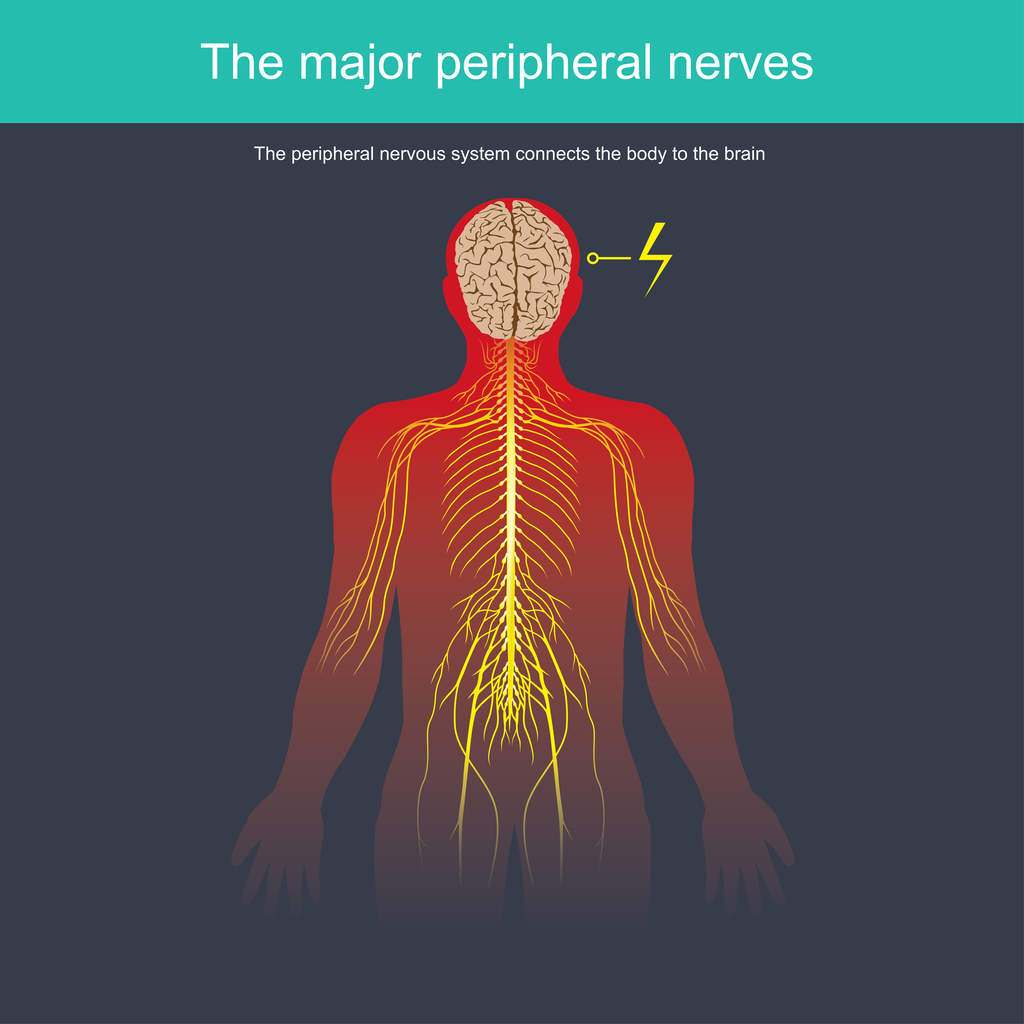
SFN develops when the small fibers of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) are damaged. These narrow nerve fibers can be found in the skin and other organs. In the skin, they process information regarding pain and temperature. In other organs, the fibers regulate autonomic functions, such as heart rate and breathing.
Symptoms
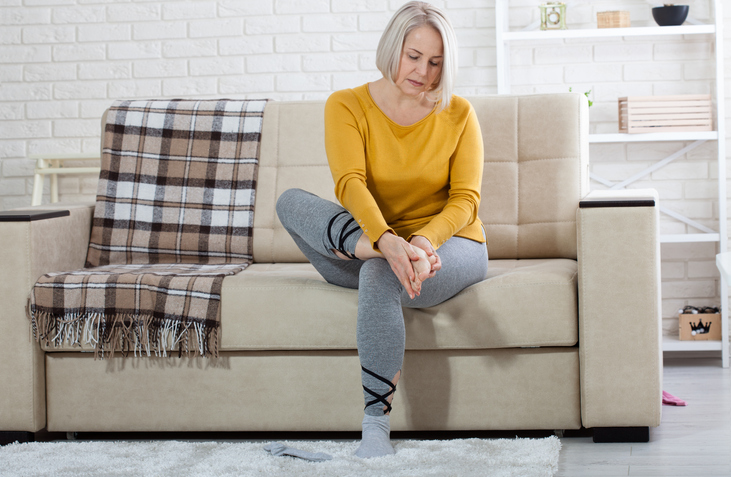
Symptoms of small fiber neuropathy vary, but pain, paresthesia, and loss of sensation (numbness) are the most common symptoms. Symptoms differ according to whether SNF is limited to the narrow fibers of the skin or if it also affects the narrow fibers of other organs.
Symptoms of SNF in the skin include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Skin discoloration
- Hyperalgesia
- Allodynia
- Difficulty telling the difference between hot and cold
- Pain triggered by temperature changes
Symptoms of SNF in other organs include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Constipation
- Difficulty sweating
- Dizziness
- Dry eyes or mouth
- Incontinence
- Rapid heart beat/palpitations
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Fainting
- Sexual dysfunction
Causes
SFN can be idiopathic (no known cause). It can also be caused from genetic mutations of the SCN9A and SCN10A genes or develop as a result of another medical condition. Diabetes is the most common medical condition associated with the development of SFN.
Other medical conditions that may cause small fiber neuropathy include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Endocrine and metabolic disorders
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Sarcoidosis
- Scleroderma
- Sjogren’s syndrome
- Immune system disorders
- Celiac disease
- Psoriasis
- Hepatitis C
- HIV
- Lyme disease
- Kidney disease
Other possible causes include:
- Vitamin B-12 deficiency
- Alcoholism
- Exposure to chemotherapy drugs
- Exposure to certain medications
Risk factors
Risk factors for developing SFN include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Male
- Mutations of SCN9A and SCN10A genes
- A parent with mutations of SCN9A and SCN10A genes
- Diabetes
- Endocrine or metabolic disorders
- Over the age of 65