Treatments
What to Expect During a Biofeedback Session

What is biofeedback?
Biofeedback is a type of therapy that involves the use of technology to monitor involuntary body responses, such as heart rate and perspiration, with the goal of learning to control these responses in order to improve a mental or physical health condition.
Most biofeedback sessions occur in an office of a trained biofeedback therapist, such as a psychologist, psychiatrist, physical therapist, or general physician. Biofeedback computer programs and mobile devices are also available for independent use.
What is a typical biofeedback session like?
- Introduction
During an initial biofeedback session, the chosen practitioner asks the individual seeking treatment about their symptoms, goals, medical history, and current medications. The practitioner also explains the biofeedback process and the technology involved. - Set-up and therapy
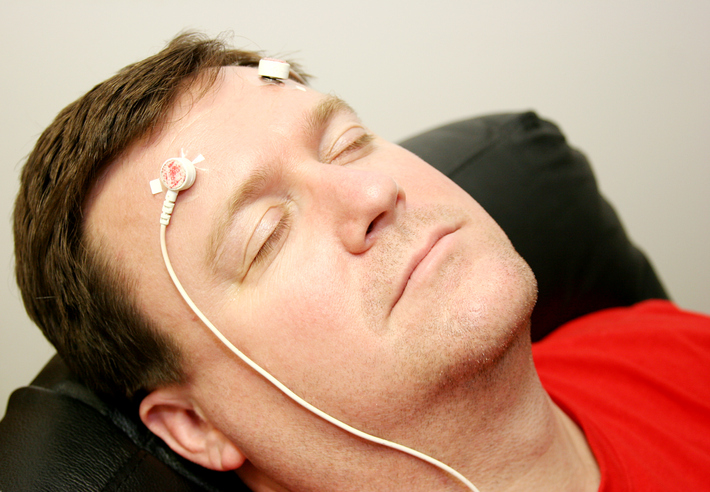
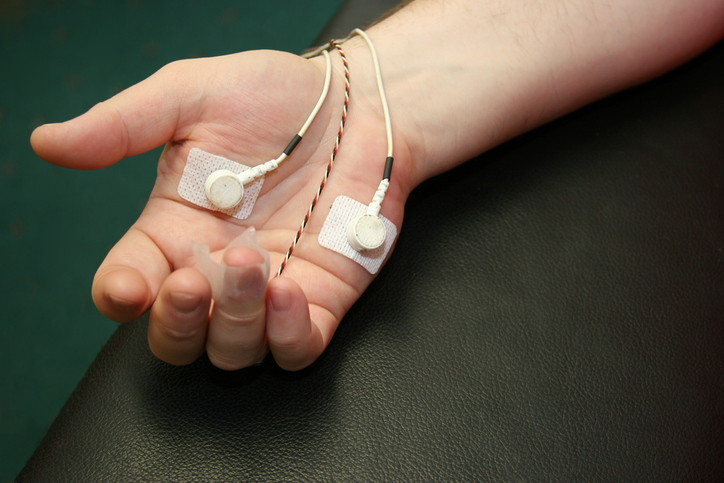
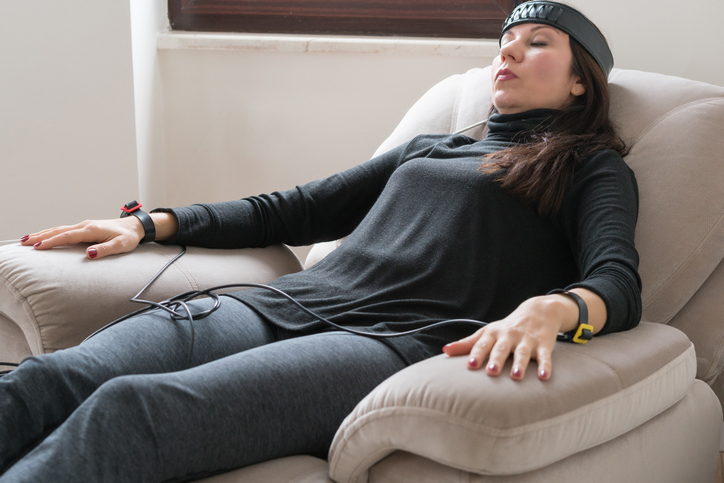
The therapist then sets up the technology that will monitor specific bodily functions for the session. Electrodes or other sensors are placed on the skin in a specific area of the body, such as a finger, the scalp, or neck. The sensors are connected to a computer or other device that provides feedback via a monitor or speakers. The feedback may be in the form of an image on the computer screen, a beeping sound, or a flashing light. - Feedback
The provided feedback can be used to identify problematic involuntary physical responses, such as tense muscles that lead to headaches. Feedback for treatment of an anxiety disorder may include changes in heart rate or perspiration when presented with stressors or other stimuli. - Strategies and techniques
The therapist then helps the individual practice relaxation techniques or learn other strategies to help control and improve problematic involuntary responses. For example, breathing exercises may be used to slow an increased heart rate or respiration. Progressive muscle relaxation may be used to ease muscle tension. Further feedback is provided as the bodily functions change in response to these strategies. The long-term goal of biofeedback therapy is to manage involuntary physical responses that lead to an exacerbation of mental or physical symptoms.
A typical biofeedback session lasts between 30 and 60 minutes. The number of required sessions depends on individual needs and goals as well as response to the treatment. At the end of each session, the practitioner typically provides the individual with practice exercises to complete at home. The primary goal of biofeedback therapy is for the individual to control problematic involuntary bodily responses (eventually, without the use of technology) in order to improve a mental or physical health condition.