Treatments
Introduction to Joint Replacement Surgery

Joint replacement surgery is a viable treatment option often considered after physical therapy and medications have not helped with joint pain. It can reduce pain, improve mobility and correct deformity. Joint replacement surgery may be recommended if severe joint pain, muscle weakness, limited motion, joint swelling and joint stiffness have failed to respond to other treatments.
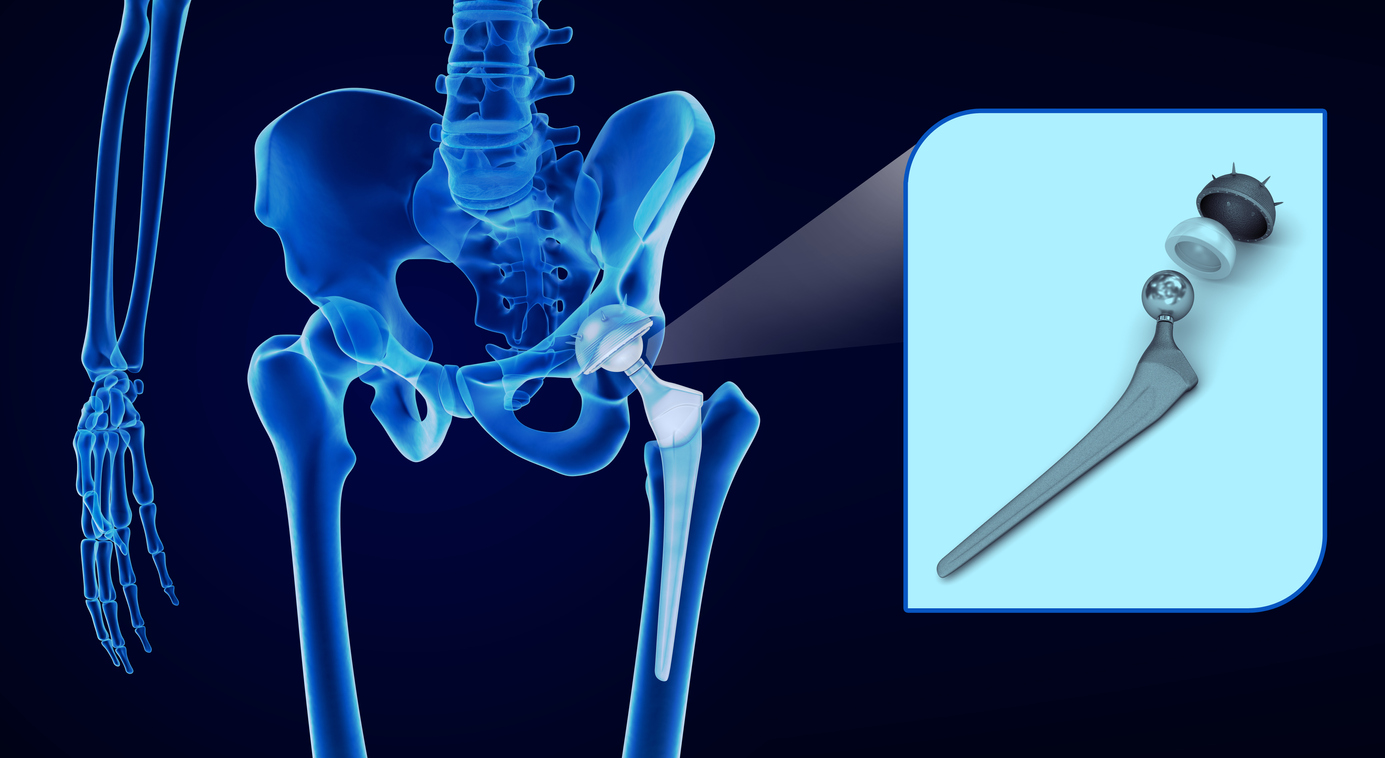
Joint replacement surgery replaces damaged cartilage and/or bone loss. Replacement joints are made from titanium, cobalt chrome, stainless steel, ceramic material or plastic. The prosthesis joint is either attached to bone with acrylic cement or press-fitted, allowing bone to grow into the implant. After a successful joint replacement surgery, physical therapy is usually prescribed to aid in proper mobilization of the replaced joint.
The most common locations for joint replacement surgery are the hips, knees and shoulders. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the most common conditions that may lead to joint replacement surgery.