Pain
The Rare Types of Neuropathy (Nerve Pain)
What is neuropathy?
Neuropathy involves damage or dysfunction of one or more nerves in the body. The condition can affect any nerve. There are four categories of neuropathy, which include the following:
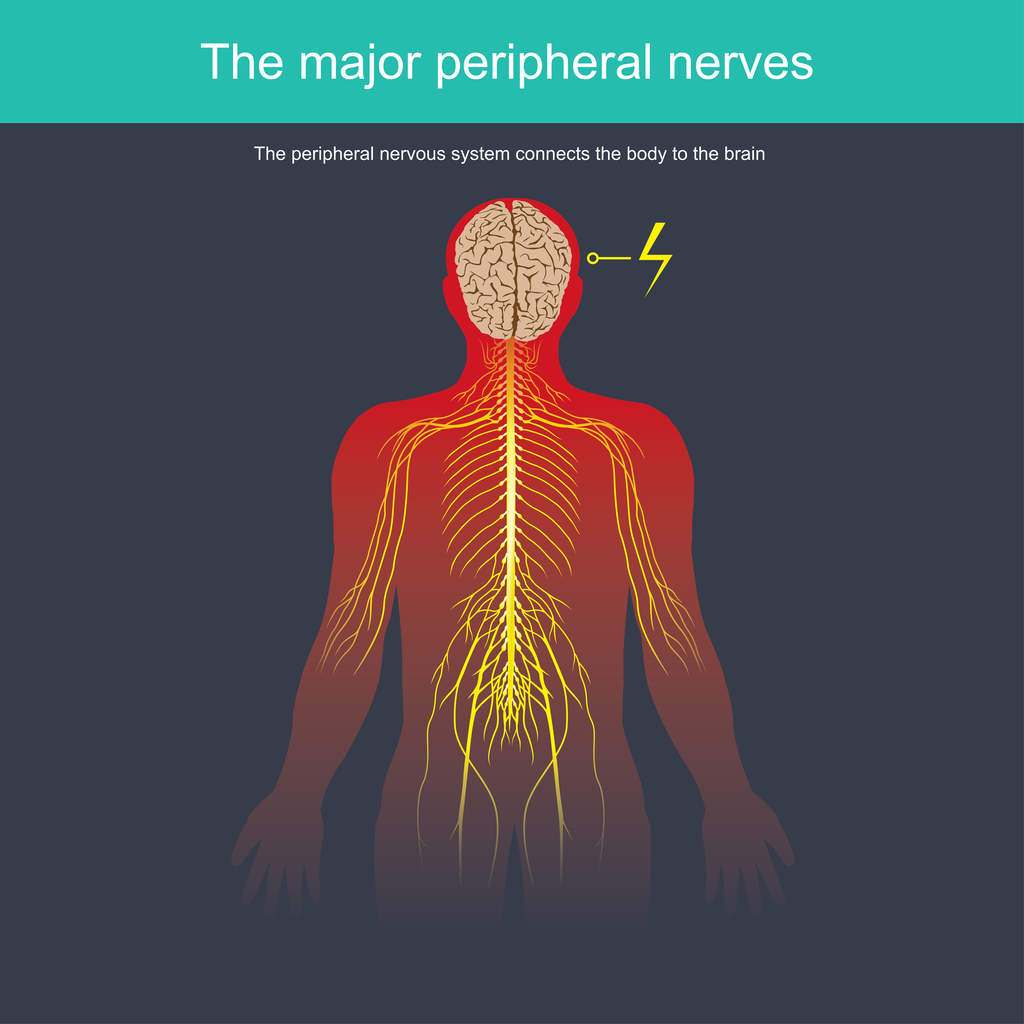
- Peripheral neuropathy affects the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, such as those in the feet, hands, legs or arms.
- Cranial neuropathy affects the cranial nerves that emerge directly from the brain.
- Autonomic neuropathy affects nerves of the involuntary nervous system, such as those that control the digestive tract, heart, and other organs.
- Focal neuropathy affects one nerve, one group of nerves, or one area of the body.
Neuropathy can present in three ways: signals failing to be sent, signals being sent when they should not be, and distortion in messages being sent. Most cases of neuropathy are polyneuropathy, impacting multiple nerves, although in cases of mononeuropathy, only one nerve is affected.
There are over 100 types of neuropathy that have been identified, impacting the motor, sensory, and autonomic nerves. Below are some of the rarest types of neuropathy.
Brachial neuritis
Brachial neuritis affects the lower nerves of the brachial plexus, which are nerves in the shoulder that sends signals from the spinal cord to the arms and hands. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, weakness, paralysis, or lack of muscle control in one shoulder and upper arm. This may occur due to an injury or without an explanation. Brachial neuritis normally resolves between a few months up to a few years.
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia
This manifestation of neuropathy occurs in the back of the throat, tongue or ears. When the glossopharyngeal nerve is damaged, intense, electric shock-like pain is experienced in the affected area. It often begins with short, mild attacks and progresses to long periods of intense pain.
Ocular neuropathic pain
Also referred to as corneal neuropathic pain, ocular neuropathic pain is normally a result of damage to the corneal nerves. Symptoms may include dry eye, burning sensation, increased tear production, photosensitivity, and the sensation of having a foreign object in the eye.
Optic neuritis
Optic neuritis is defined as damage to the optic nerves, which transmit visual data from the eye to the brain. It is the result of inflammation. Symptoms may include temporary vision loss, pain in the eye, loss of color vision, flashing lights with eye movements, and pain with eye movements.
Vestibular neuritis
Vestibular neuritis occurs when the vestibulocochlear (inner ear) nerve is damaged from inflammation or swelling. This can cause dizziness, vertigo, nausea, motion sensitivity, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. Vestibular neuritis can be chronic or acute.
Additional source: American Academy of Ophthalmology EyeWiki