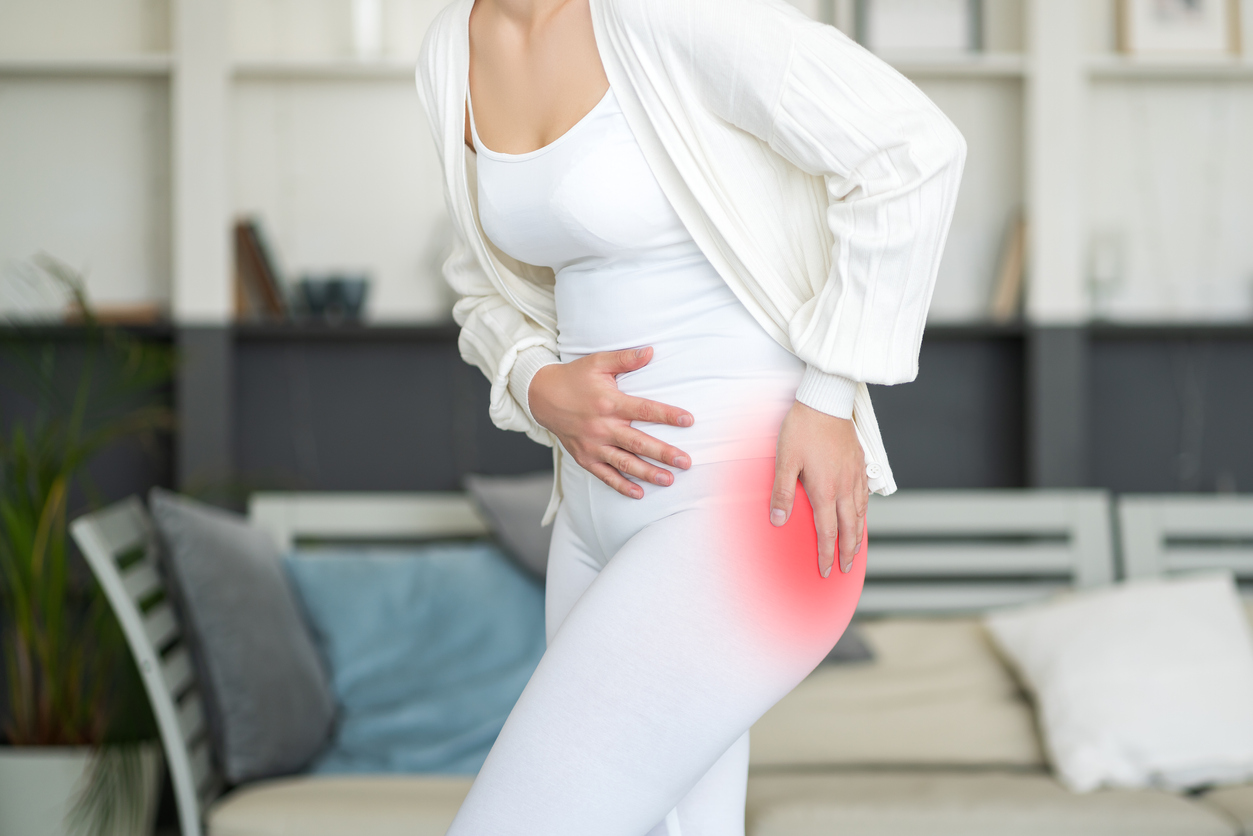
Pain
What Is Bursitis?

Bursitis is a painful, and normally temporary, condition that occurs when a bursa becomes inflamed or irritated. Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that act as a cushion to reduce friction between the bones, tendons and muscles that are located near joints. Most bursae are located near larger joints that perform repetitive motion.
Types of bursitis
Bursitis usually affects the Achilles tendon, buttocks, elbow, hip, knee, or shoulder. There are various types of bursitis, depending on the area impacted. The most common types of bursitis include the following:
- Retromalleolar tendon
- Posterior Achilles tendon
- Hip
- Elbow
- Knee
- Kneecap
Symptoms
The most common symptom of bursitis is pain. The pain can be sudden and severe, or may increase slowly. Typically, pain is experienced when stretching or extending the affected joint. Limited range of motion occurs with or without pain.
Although each person may experience different symptoms, the most common symptoms of bursitis include the following:
- Achy or stiff joints
- Swelling or redness at the joint area
- Pain when moving or pressing on the joint
- Joint tenderness
- Limited motion in the joint area
Repeated occurrences of pain, swelling and tenderness may result in chronic bursitis. Muscle deterioration and loss of range of motion can be caused by chronic bursitis.
When to contact a physician
Consult a healthcare provider if the following occur:
- Fever that is over 102 degrees Fahrenheit (39 degree Celsius)
- Excessive swelling, redness, bruising, rash or warmth in the affected area
- General overall illness
- Multiple painful areas
- Inability to move the affected joint
- Pain that lasts longer than two weeks
- Sharp or shooting pain, especially when exerting oneself
Causes
The most common cause of bursitis is repetitive motions. High-risk activities include carpentry, gardening, raking, painting, scrubbing, tennis, repeated lifting or throwing, and golf. Other causes of bursitis include the following:
- Injury or trauma to the affected area
- Infection, especially with Staphylococcus aureus bacteria
- Sitting or standing in the wrong position for extended periods
- Lack of stretching prior to exercise
- Leaning on the elbow for long periods
Risk factors
Bursitis is common in adults, especially after age 40. Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing bursitis, which include the following:
- Age. As tendons become less elastic and easier to tear with age, the risk of developing bursitis increases.
- Existing conditions. The risk of bursitis is greater due to certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, tendonitis, thyroid disease, psoriatic arthritis, and diabetes.
- Weight. The risk of hip and knee bursitis increases in individuals who are overweight.
- Lifestyle. Hobbies or occupations requiring repetitive motion or pressure on certain bursae increase the likelihood of bursitis occurring.
- Existing structure issues. Existing problems with the structure of a bone or joint increase the odds of a bursitis occurrence.