Treatments
What Is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)?

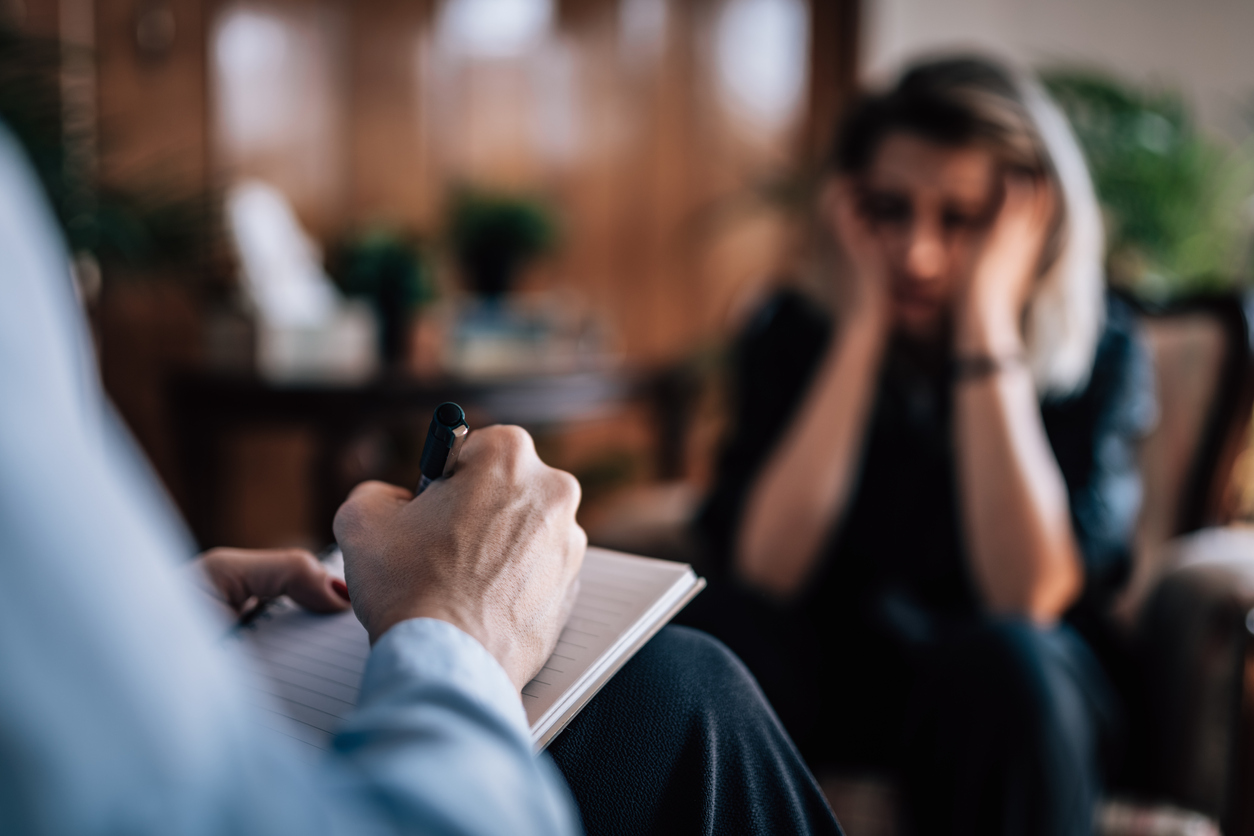
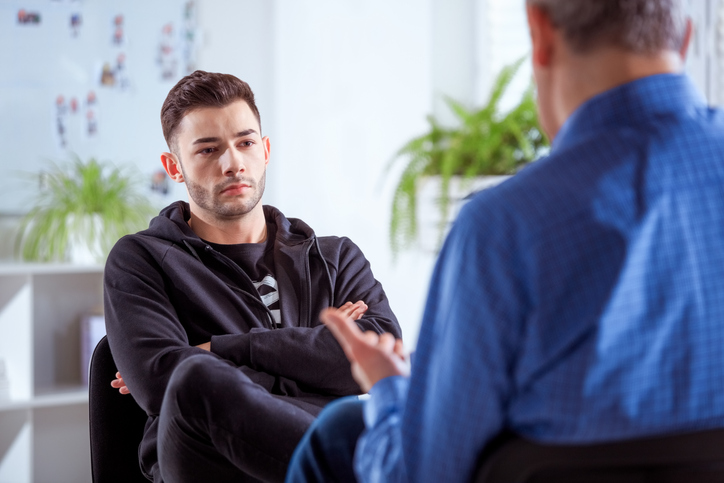
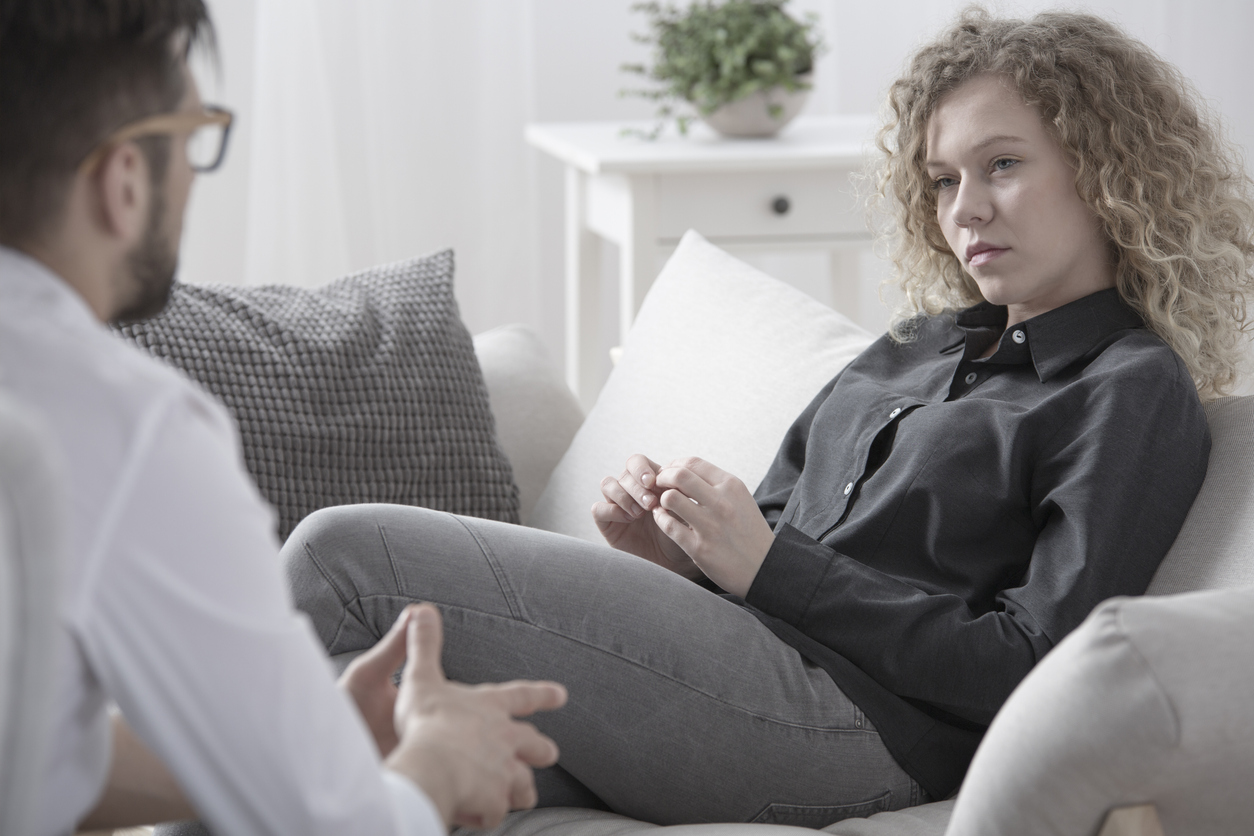
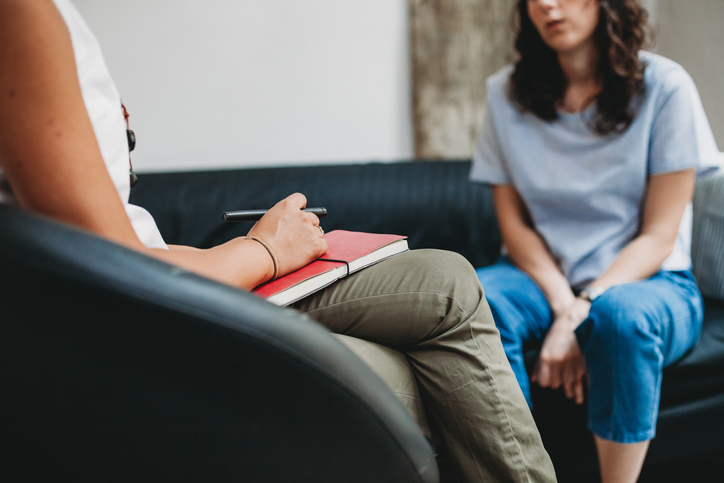
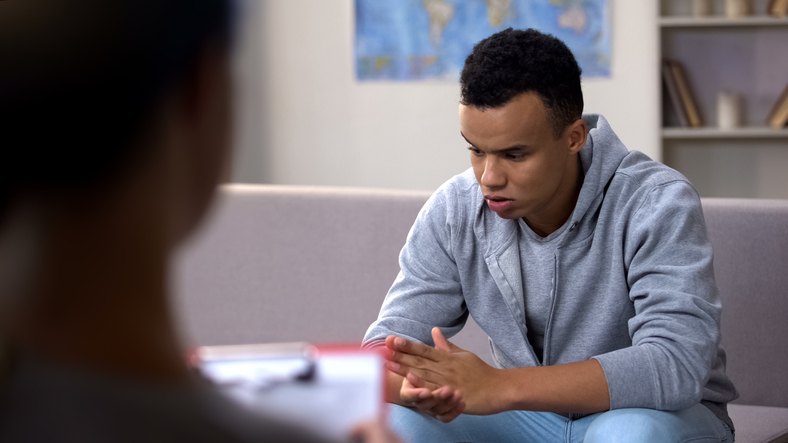
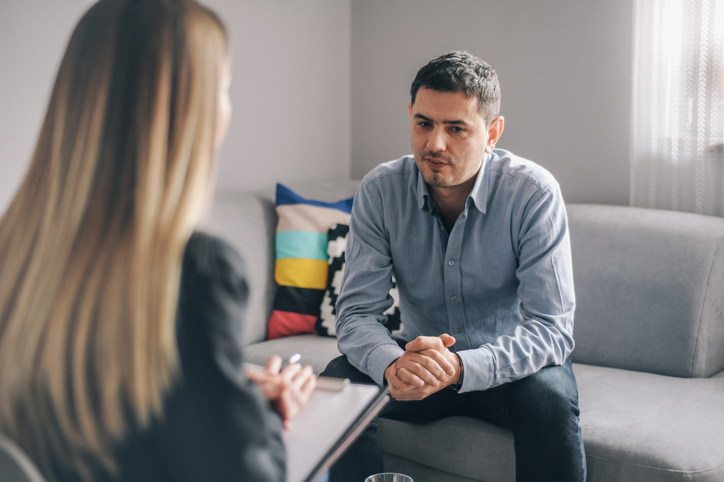
Cognitive behavioral therapy, or CBT, is a common type of psychotherapy; it is a combination of cognitive therapy, which focuses on moods and thoughts, and behavioral therapy, which focuses on actions and behaviors. It involves learning how to identify and change inaccurate or negative thoughts and behavioral patterns in order to respond to stressful situations in a more effective way.
CBT is an effective treatment for various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, eating disorders, and post-traumatic stress disorder. It is also beneficial for anyone learning to better manage stressful situations.
Cognitive behavioral therapy commonly involves 4 steps:
- Identifying troubling conditions or situations
During this first step, an individual works with a therapist to identify the issues they would like to address. Goals are also created. - Becoming aware of thoughts and beliefs surrounding the issue
The therapist encourages the individual to discuss their issues and share their thoughts and beliefs that surround them. - Identifying inaccurate or negative thinking
The individual works with the therapist to identify physical, emotional, and behavioral responses to different situations. Patterns of thinking are identified. - Reshaping thought and behavior patterns
The therapist works with the individual to change negative thoughts and behaviors that are based on false perceptions, which helps in the development of positive coping behaviors.
Cognitive behavioral therapy is considered a short-term therapy — participating in five to 20 sessions is usually sufficient. Activities to complete outside of therapy sessions, such as journaling, reading articles, or completing worksheets, may be assigned.
While cognitive behavioral therapy may not cure a condition or eliminate a challenging situation, it can be an excellent tool for coping in a healthy way, leading to an improved quality of life.