Treatments
What Is Peripheral Nerve Surgery?

What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
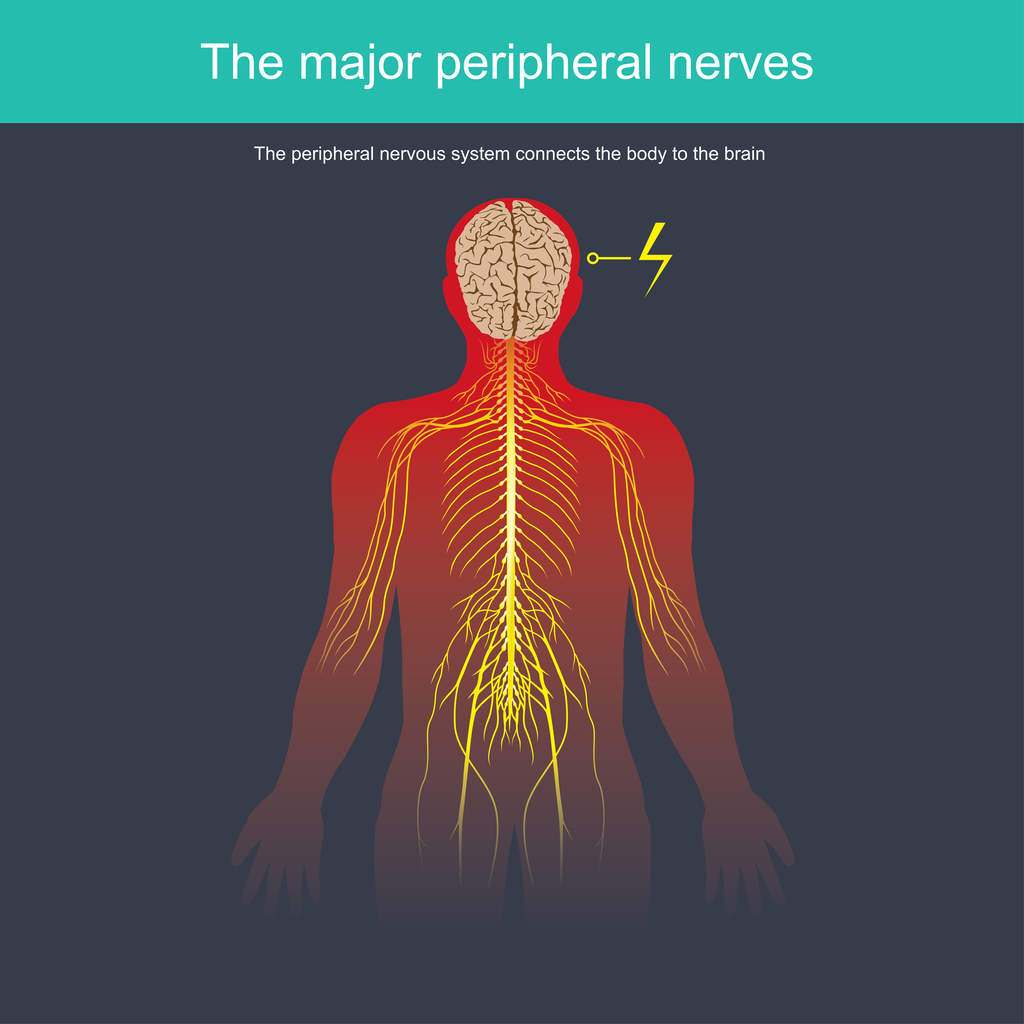
Peripheral neuropathy is a medical condition that develops when the peripheral nerves are damaged. The peripheral nervous system is the communication network connecting the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) to every other body part. Approximately 20 million people in the United States have some type of peripheral neuropathy. It can cause pain, numbness, and weakness. It may also affect other bodily functions, such as urination, digestion, heart rate, sweating, and blood pressure.
Peripheral Nerve Surgery
There are conventional or alternative and complementary treatment options for Peripheral neuropathy. Individuals may consider peripheral nerve surgery once those treatment options have been attempted. The exact methods for the surgery will differ depending on the condition or nerve being treated. The surgery may include nerve grafting, nerve transfers, nerve repair, nerve decompression, or nerve reconstruction. Microsurgical and endoscopic techniques may be used to ensure precision and decrease the likelihood of tissue trauma.
Multiple surgeons may participate, depending on where in the body the nerve injury occurred or the type of surgery. Specialists who can participate include neurosurgeons, plastic and reconstructive surgeons, orthopedic surgeons, and others.
What does Peripheral Nerve Surgery Treat?
Some of the peripheral neuropathies or peripheral nerve injuries that can be treated via surgery include:
- Nerve entrapment syndromes such as carpal tunnel syndrome, tarsal tunnel syndrome, etc.
- Nerve injuries due to tumors such as schwannomas or Neurofibromas
- Nerve injury from trauma such as brachial plexus injuries
Recovery Time
Recovery from the surgery takes time, months, or longer. The exact recovery length depends on the distance nerve fibers need to grow, as nerves grow at the rate of one inch per month.
Additional Source University of Michigan Health