Pain
Conventional Medical Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
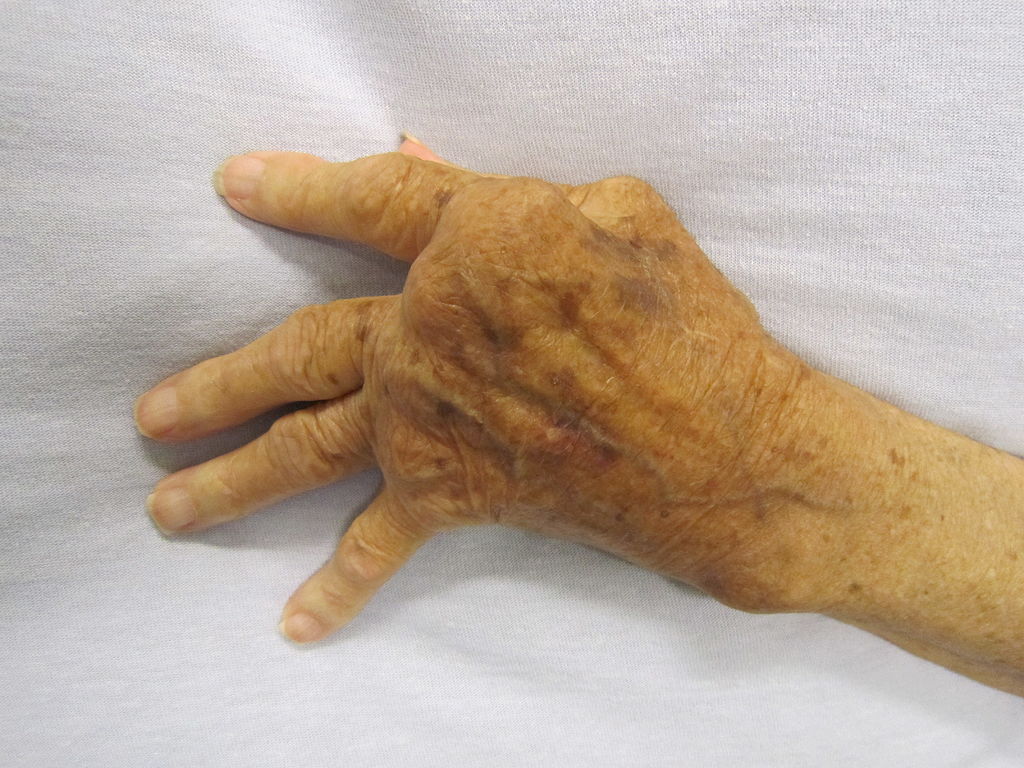
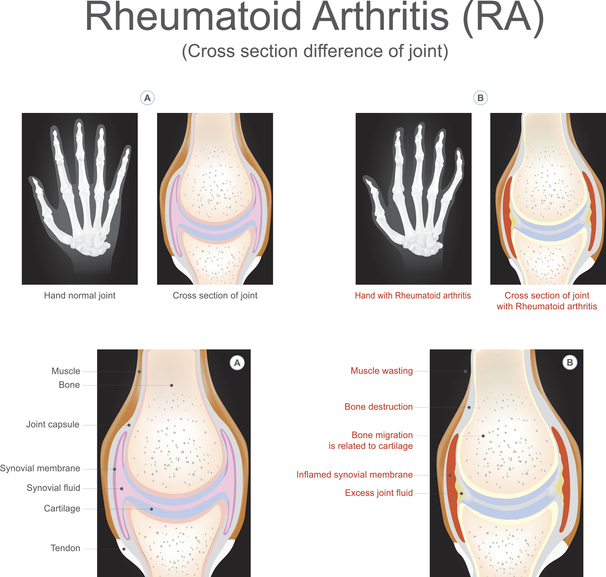
Rheumatoid arthritis, or RA, is a chronic, inflammatory autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues. Rheumatoid arthritis causes inflammation in the lining of the joints; eventually, this inflammation can lead to bone erosion and joint deformity. The condition can affect any joint in the body, including joints in the hands, elbows, feet, hips, jaw, knees, neck, shoulders and wrists. Rheumatoid arthritis presents in a symmetrical pattern; it develops in the same joints on both sides of the body, such as both shoulders or both knees. RA can affect more than the joints; it can also affect other body parts and systems including, but not limited to, the eyes, skin, heart, lungs or blood vessels.
Conventional medical treatments
No cure currently exists for rheumatoid arthritis; however, early treatment can aid with symptom management. Treatment plans depend on the length of time RA has been present and symptom severity. Rheumatoid arthritis treatments include the following:
Over-the-counter medications
- Acetaminophen can be purchased over-the-counter as an oral medication. It is used to treat mild to moderate pain but does not have any anti-inflammatory benefits. Only one medication containing acetaminophen should be taken at a time.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen sodium, can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
Prescribed medications
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as celecoxib, nabumetone, piroxicam, ibuprofen, or naproxen sodium, may be prescribed to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Diclofenac/misoprostol is a prescribed oral medication that combines the NSAID diclofenac with misoprostol. This medication also helps prevent stomach ulcers that may result from perpetual use of NSAIDs.
- Corticosteroid medications, such as prednisone, can slow joint damage and reduce inflammation. Corticosteroids are often prescribed to relieve acute symptoms and are gradually tapered.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as methotrexate, leflunomide, hydroxychloroquine, minocycline and sulfasalazine, are prescribed medications that can slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and reduce permanent joint damage.
- Biologic agents, also known as biologic response modifiers, are a newer class of DMARDs and include abatacept, adalimumab, anakinra, baricitinib, certolizumab, etanercept, golimumab, infliximab, rituximab, sarilumab, tocilizumab and tofacitinib. Biologics are injectable medications that target parts of the immune system that trigger inflammation. Biologic DMARDs are most effective when paired with a nonbiologic DMARD.
- Janus associated kinase inhibitors, such as tofacitinib or baricitinib, may be prescribed if DMARDs or biologics are not effective. This medication affects genes and immune cell activity to prevent inflammation and stop joint damage.
- Immunosuppressants, such as cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, cyclosporine and hydroxychloroquine, come in both oral and injectable forms. This medication works by suppressing the body’s immune system response.
- Opioid pain medications, such as codeine, fentanyl, hydrocodone, oxycodone, tramadol and morphine, may be prescribed to treat pain associated with RA.
Topical medications
- Topical capsaicin is an over-the-counter cream used to relieve mild pain caused by RA.
- Diclofenac sodium topical gel is a topical NSAID that can relieve joint pain.
- Diclofenac sodium topical solution is used to ease knee pain.
Physical therapy
A physical or occupational therapist can provide exercises to keep the joints flexible.
Surgical options
- Synovectomy is a surgery that removes the inflamed joint lining of the knees, elbows, wrists, fingers or hips.
- Tendon repair may be needed if a damaged joint causes tendons around the joint to loosen or rupture.
- Joint fusion is a surgical procedure that fuses a joint to stabilize or realign it. This can also help with pain relief if joint replacement is not an option.
- Total joint replacement removes the damaged parts of a joint and replaces it with a prosthesis made of metal and plastic.