Pain
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
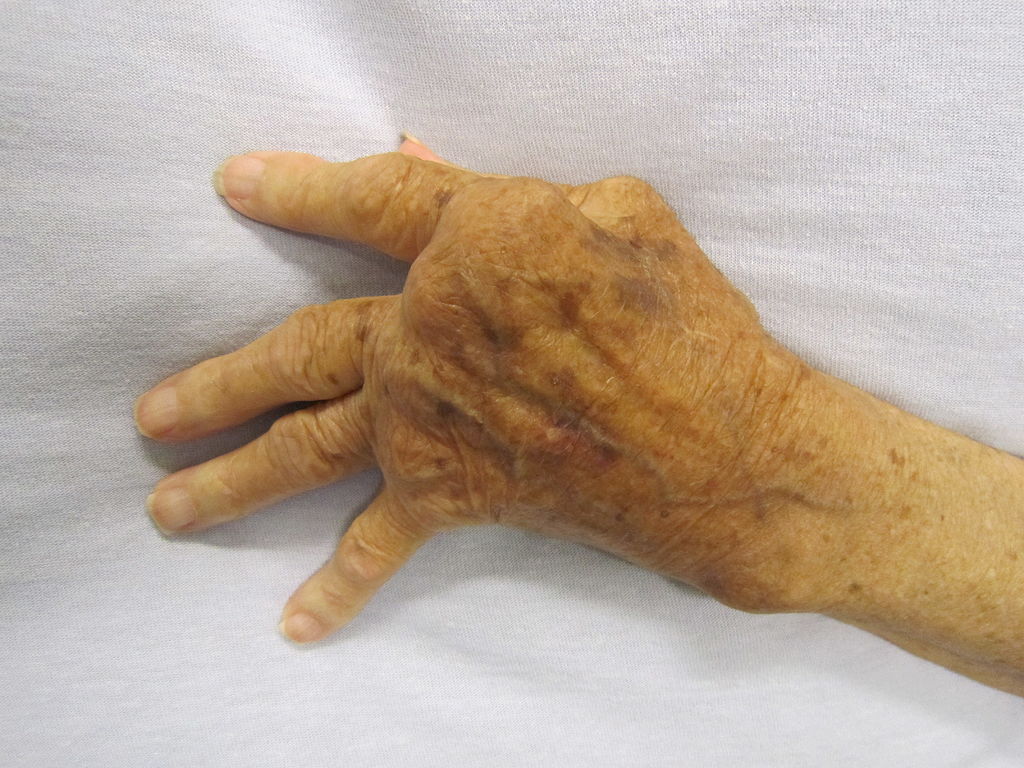
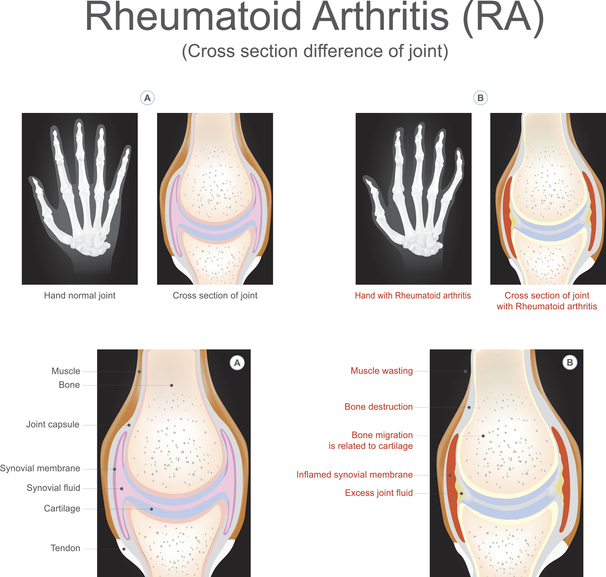
Rheumatoid arthritis, or RA, is a chronic, inflammatory autoimmune disorder in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues. Rheumatoid arthritis causes inflammation in the lining of the joints; eventually, this inflammation can lead to bone erosion and joint deformity. RA can affect any joint in the body, including joints in the hands, elbows, feet, hips, jaw, knees, neck, shoulders and wrists. RA presents in a symmetrical pattern; it develops in the same joints on both sides of the body, such as both shoulders or both knees. RA can also affect more than the joints; it can also affect other body parts and systems including, but not limited to, the eyes, skin, heart, lungs or blood vessels.
What are the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis?
The symptoms of RA vary from person to person. While some people can go long periods with little or no symptoms (remission), others experience flares (an increase in symptoms) and are symptomatic for months at a time. Symptoms of RA that present in the joints include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Stiffness
- Swelling
- Pain
- Redness or warmth
Other symptoms of RA include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Fatigue
- Muscle aches
- Poor appetite
- Malaise
- Depression
- Hoarseness of the voice
Who is at risk of developing RA?
While rheumatoid arthritis can develop at any age, it most commonly begins during middle age, and women are more likely than men to develop the condition. Family history also plays a role in the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. If one member of the family has RA, other family members have an increased risk of developing it. Smoking also increases the risk of developing RA and is associated with greater disease severity. Exposure to toxins, such as asbestos or silica, may also increase the risk for RA. Finally, individuals who are overweight (particularly women 55 and younger) may be at a higher risk of developing RA.