Treatments
Medication Treatments for Neuropathic Pain Relief

What is neuropathic pain?
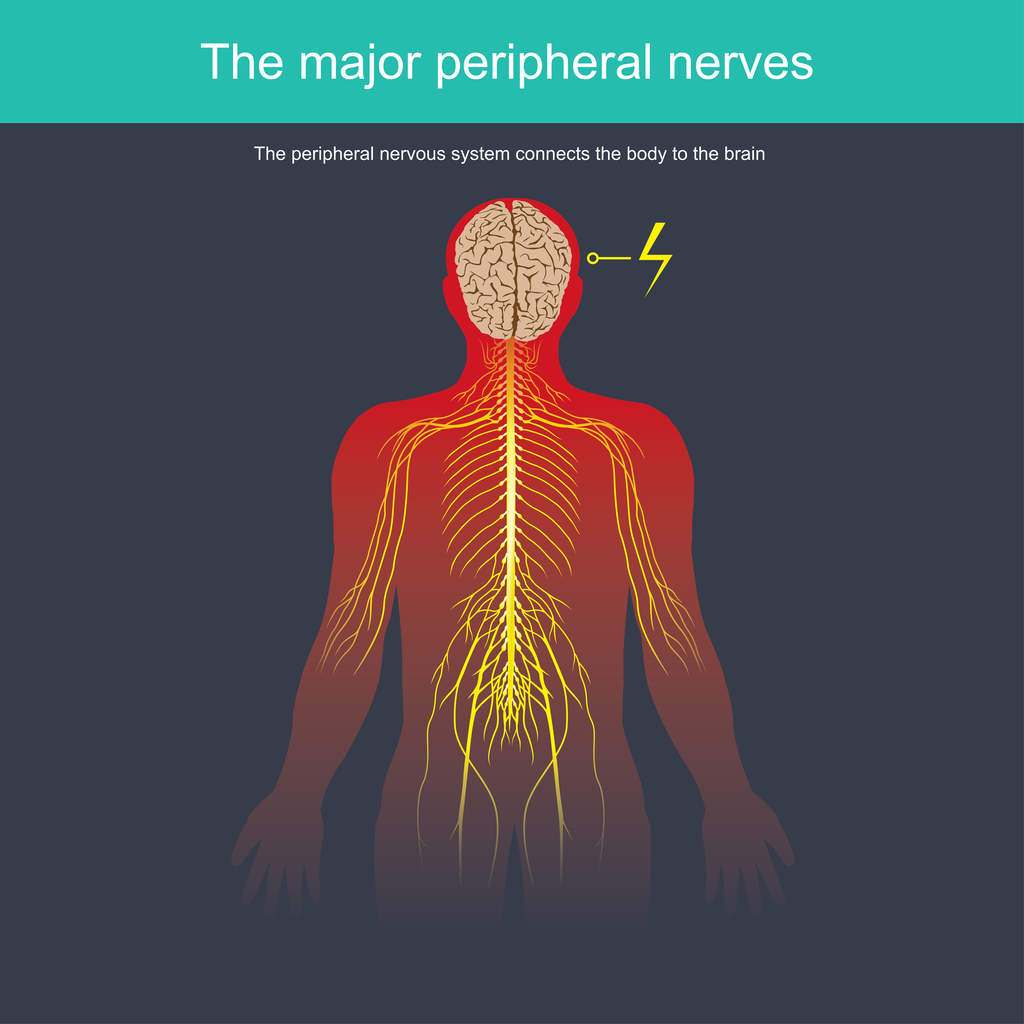
Neuropathic pain occurs when the central nervous system or the peripheral nerves are damaged. Peripheral neuropathy usually begins in the longest nerves of the body, such as the feet and hands. As the condition progresses, it moves up the arms and legs.
Because the spine and nerves are intertwined and work together, issues in the spine can cause nerve pain. Lumbar herniated disc is a common form of nerve pain that occurs when a disc between the vertebrae becomes herniated and places pressure on a spinal nerve root. Once the nerves become damaged and neuropathy becomes an issue, false signals are sent from the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system to the spinal cord, and then to the brain.
Medication treatment for neuropathic pain
Medical treatment for neuropathic pain is dependent on the cause, severity, side effects, and other factors. There are various medications that can help ease nerve pain. Finding the right medication, or combination of medicines, is often trial and error. A low dose is usually prescribed and can be increased when side effects and effectiveness are determined.
Anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs)
Anti-epileptic drugs, or AEDs, include medications that calm nerve pain, such as anti-seizure, anticonvulsant, and neuroleptic medicines. They are frequently prescribed to treat neuropathic pain. Common forms of anticonvulsants include carbamazepine, gabapentin and oxcarbazepine. These medications interfere with pain signals by decreasing nerve impulses. Side effects associated with using anticonvulsants to relax nerves may include constipation, chest pain, drowsiness, nausea, heart problems, and allergic reactions.
Antidepressant medicines
Chronic pain not only affects physical health, but can also affect mental health. Depression can increase chronic pain levels, and chronic pain symptoms can worsen depression. Antidepressant medications are a treatment option for neuropathic pain and depression.
Commonly prescribed antidepressants for neuropathic pain include the following:
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Combination therapy
Side effects associated with antidepressants include heart issues, constipation, lightheadedness, weight gain, nausea, dry mouth, and drowsiness. They may also increase the risk of suicidal thoughts.
Topical remedies
Topical medications are available in cream, patch or gel form. They are beneficial for treating localized pain, or pain located in a particular region of the body. Once the medication is absorbed into the skin, it works by relieving pain or numbing the area.
Topical medications are a good option for those who cannot take pills. Very little of the drug is absorbed into the bloodstream; therefore, cognitive side effects are usually avoided. Commonly prescribed topical medications include capsaicin and lidocaine. Side effects include swelling, burning or flushing of the face or skin. Other side effects may include breathing difficulties and wheezing.
Opioids
An opioid, or narcotic, is a medication prescribed to relieve moderate to severe pain by weakening pain signals that travel from the nerves to the brain. Opioids are prescribed to treat moderate to severe pain that does not respond well to other treatment options. They block pain signals by attaching to opioid receptors in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. As pain messages are modified, less pain is experienced.
Opioids have the potential to be abused and can be addictive. Use should be carefully monitored by a pain specialist. Side effects may include vomiting, constipation, nausea, diarrhea and drowsiness. Breathing problems may also occur in some cases.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroid medications, such as prednisone, can reduce neuropathic pain by decreasing inflammation. They can be administered via skin creams, drops, patches, pills or injections. Potential side effects include mood swings, weight gain, muscle weakness, blurred vision, or increased thirst.