Treatments
Treat Neuropathic Pain With Anticonvulsants

What is neuropathic pain?
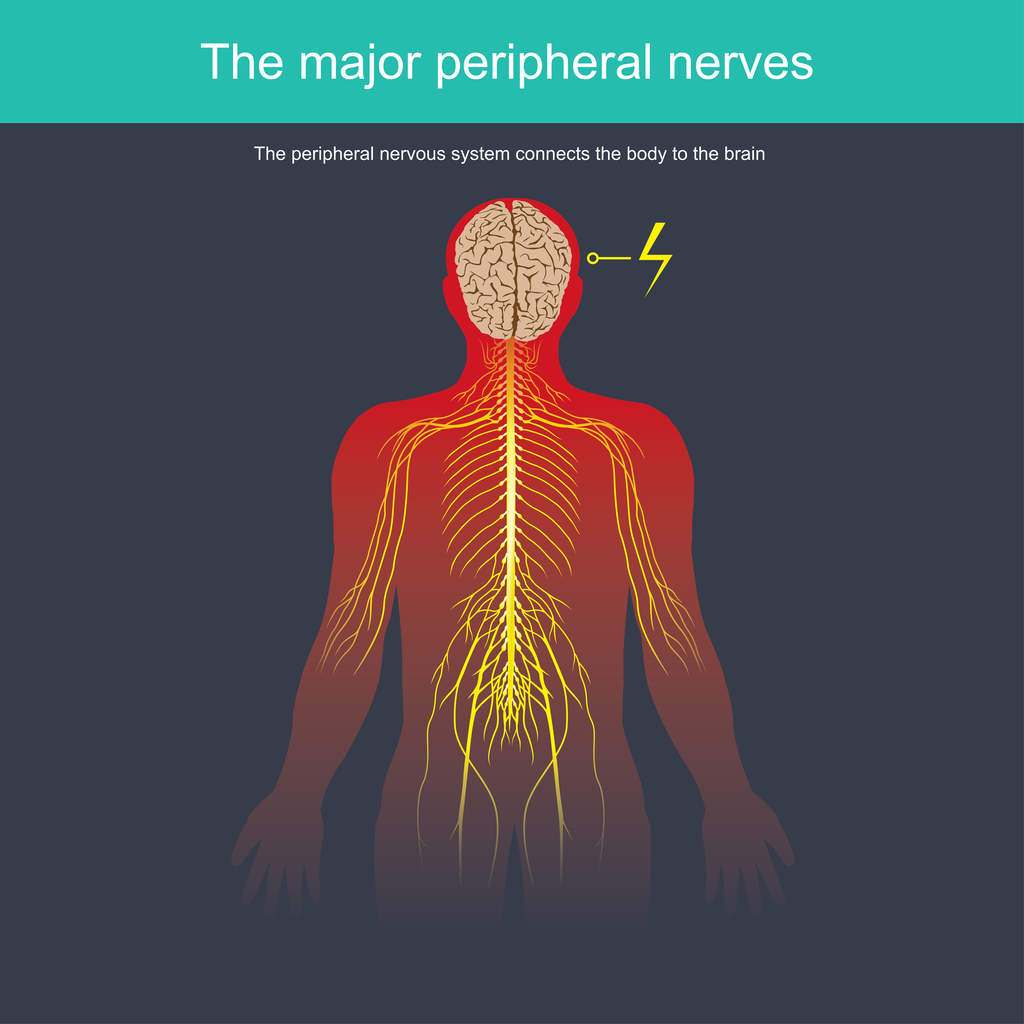
Neuropathic pain occurs when the central nervous system or the peripheral nerves are damaged. Peripheral neuropathy usually begins in the longest nerves of the body, such as the feet and hands. As the condition progresses, it moves up the arms and legs.
Because the spine and nerves are intertwined and work together, issues in the spine can cause nerve pain. Lumbar herniated disc is a common form of nerve pain that occurs when a disc between the vertebrae becomes herniated and places pressure on a spinal nerve root. Once the nerves become damaged and neuropathy becomes an issue, false signals are sent from the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system to the spinal cord, and then to the brain.
What are anticonvulsants?
Anticonvulsants are prescription medicines that calm brain hyperactivity and treat seizure disorders. They have also been known to reduce chronic pain. Anticonvulsants relieve pain by interfering with damaged or overly sensitive nerve signals. They reduce or control abnormal increases in brain electrical activity.
Anticonvulsants are used to alter or control excitability of neurons. They may relieve chronic pain for some people, but not for others. They have nerve-calming qualities that can help soothe burning, stabbing or shooting pain resulting from nerve damage.
Anticonvulsants for neuropathic pain
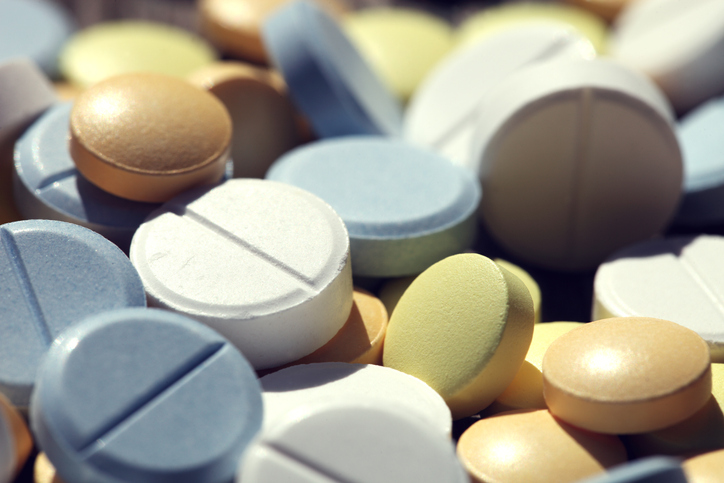
Anticonvulsants are often the first choice of treatment for neuropathic pain and are frequently prescribed for it. Common forms of anticonvulsants include carbamazepine, pregabalin, gabapentin, topiramate and oxcarbazepine.
Side effects may include constipation, chest pain, drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, nausea, heart problems, feet or leg swelling, and allergic reactions. It is often recommended to begin with a low dose and slowly increase it to reduce side effects.
The kidneys remove these medications from the body; therefore, the dose should be adjusted if kidney function is weakened. Side effects may also be amplified due to impaired kidney function. Lower doses are typically safe to use with kidney disease.