Pain
Mexiletine as a Treatment for Neuropathic Pain

What is mexiletine?
Mexiletine is an antiarrhythmic drug primarily used to treat irregular heartbeats. It is an oral form of lidocaine. In addition to restoring normal heart rhythm, it may reduce certain types of neuropathic pain, particularly peripheral neuropathy.
How it works
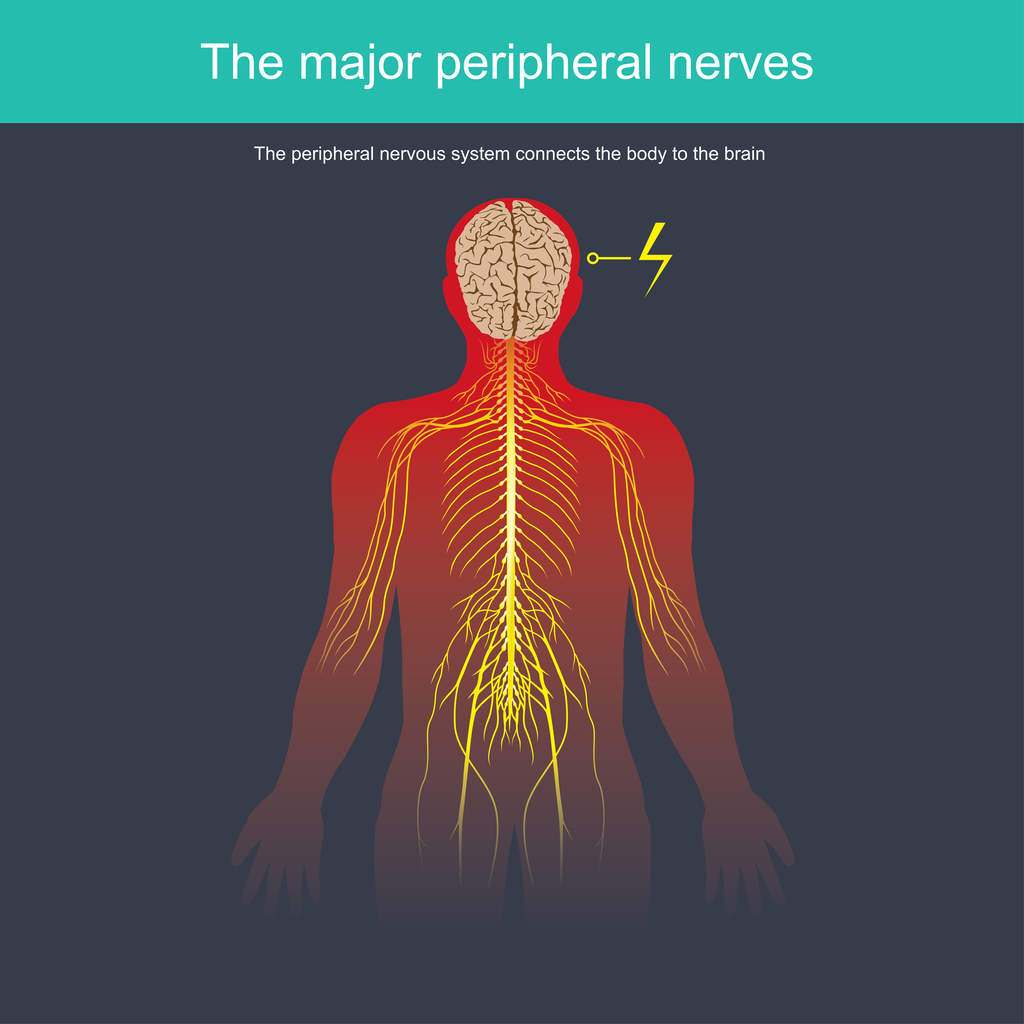
Mexiletine is thought to reduce neuropathic pain by adhering to peripheral nerves and limiting their pain signals traveling to the brain and central nervous system. Pain is decreased as this medication bonds to the peripheral nerves over time. Research has shown that it can provide modest pain relief without causing adverse effects.
Potential side effects
Seek immediate emergency care if signs of an allergic reaction occur, which includes the following: hives; difficulty breathing; swelling of the throat, face, lips or tongue. Other possible side effects include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Upset stomach, nausea, or vomiting
- Dizziness
- Heartburn
- Nervousness
- Blurred vision
- Coordination problems
Serious sides effects that require medical treatment include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Chest pain
- Liver problems
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Itching
- Dark-colored urine
- Clay-colored stool
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes
- New or a worsening irregular heartbeat
Takeaway
Studies involving mexiletine for the treatment of neuropathic pain have been small in scale, with fewer than 400 individuals participating. Long-term studies have not been completed. Therefore, additional research and studies are needed to determine the safety and effectiveness of mexiletine as a treatment option for neuropathic pain.
Additional sources: University of Chicago Center for Peripheral Neuropathy and American Family Physician