Treatments
What Is Minimally Invasive Surgery?

Minimally invasive surgery, or MIS, is a surgical approach that causes as little trauma to the body as possible. Traditional open surgery requires large incisions through the skin and tissues, which equates to a longer hospital stay. MIS is typically a safer surgical option than traditional surgery; it involves quicker healing, shorter hospital stays, less pain, and reduced risk of postsurgical complications.
Minimally invasive surgery vs. traditional open surgery
Traditional open surgery typically involves a large incision through the skin, tissue, and in some cases, muscle to access the area that needs attention. MIS involves one or more much smaller incisions that are used as portals to insert surgical instruments and endoscopes (tubes with a lighted camera at the tip that projects images on a screen).
Non-robotic vs. robotic minimally invasive surgery
Minimally invasive surgery can be categorized as either non-robotic or robotic. During non-robotic surgery, a surgeon uses their hands to operate and manipulate surgical tools, whereas during robotic surgery, a surgeon operates robotic arms from a console. Robotic surgery allows for smaller, more precise movements.
Non-robotic minimally invasive surgery
Types of non-robotic minimally invasive surgeries include keyhole, endovascular, and endoscopic.
- Keyhole surgery involves small, or keyhole, incisions that are typically a half-inch long or less. These cuts are used to insert narrow surgical instruments and an endoscope. The type of endoscope used depends on the area of the body. For example, a laparoscope is used for the abdomen (laparoscopic surgery), a thoracoscope for the chest cavity (thoracoscopic surgery), and an arthroscope for joints (arthroscopic surgery).
- Endovascular surgery requires only one very small incision or needle puncture. A small catheter is inserted through the incision into a blood vessel, allowing a surgeon to pass surgical instruments though the catheter to perform the operation.
- Endoscopic surgery involves inserting surgical tools through a natural body orifice, such as the mouth or nose; therefore, incisions on the skin are not necessary. “Endoluminal” endoscopic surgery occurs within the walls of an organ, whereas “transluminal” endoscopic surgery involves cutting through an organ wall.
Robotic minimally invasive surgery
Robotic technology, which can be precisely controlled, allows a surgeon to view enlarged 3D images of the surgical site from an electronic operating station. During robotic surgery, a robot arm — operated by a specially trained surgeon — allows for greater precision in small areas.
Types of minimally invasive surgery
Some hospitals and surgical centers are not equipped for MIS, and not all types of surgery can be performed this way. Some of the most common types of minimally invasive surgeries include the following:
- Adrenal gland removal (adrenalectomy)
- Gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy)
- Appendix removal (appendectomy)
- Spleen removal (splenectomy)
- Endovascular surgery (angioplasty, atherectomy, embolization, and stenting)
- Otolaryngology (ear, nose, and throat) surgery
- Gastrointestinal tract surgeries, including tumor removal (endoscopic submucosal dissection or transanal endoscopic microsurgery) and sphincter myotomy
- Heart surgery (mitral valve repair and atrial septal defect repair)
- Removal of unhealthy parts of the colon (colectomy)
- Epilepsy treatment (stereoelectroencephalography and deep brain stimulation)
- Hiatal hernia repair (anti-reflux surgery)
- Rotator cuff tear repair (shoulder arthroscopy)
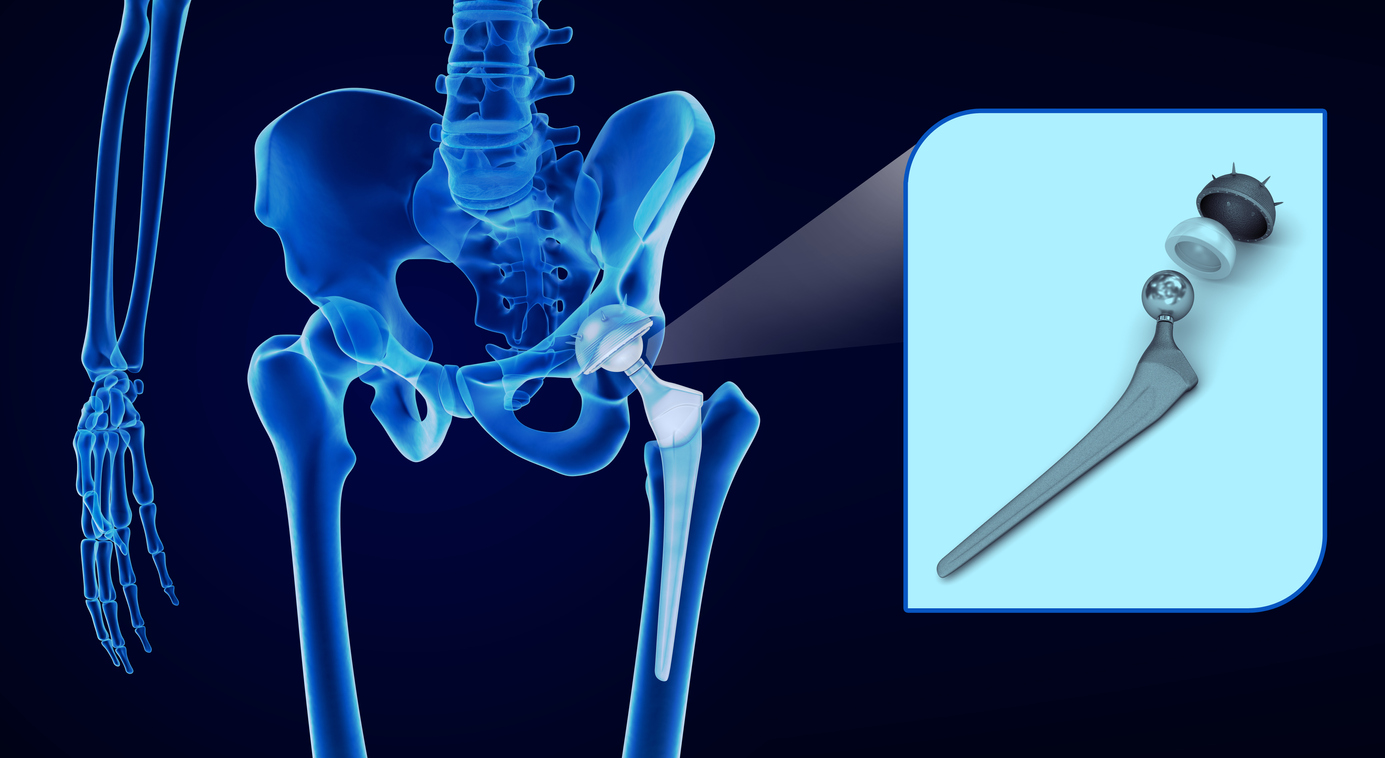
- Minor hip damage repair (hip arthroscopy)
- Spinal surgery (discectomy, laminectomy, spinal fusion, and tumor removal)
- Urologic surgery, including kidney removal (nephrectomy), prostate removal (prostatectomy) or pelvic organ prolapse repair (sacrocolpopexy)
Advantages of minimally invasive surgery
Minimally invasive surgery offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including the following:
- Less blood loss during surgery
- Reduced risk of trauma
- Less damage to skin, muscles, and tissues
- Reduced risk of surgical complications
- Shorter, less painful recovery time
- Reduced risk of infection
- Smaller, less visible scars
- Less time in the hospital
- Lower pain levels
- May not require general anesthesia
- May make surgery possible for individuals or health conditions that aren’t candidates for traditional open surgery
Disadvantages of minimally invasive surgery
Minimally invasive surgery also has disadvantages in comparison to traditional open surgery. Disadvantages include the following:
- Longer operating time (more steps, tools, and assistants required, especially for robotic surgery)
- Due to advanced preparation requirements, may not be possible in an emergency situation or when the medical condition isn’t yet clear
- Increases the risk of heart and lung complications (especially during laparoscopic surgery) in individuals with certain heart and lung conditions
Potential complications
Although MIS is typically safer than traditional surgery, any type of surgery involves the potential for complications, including the following:
- Anesthesia complications
- Excessive bleeding
- Blood clots
- Infection
- Pain at incision site
- Nerve damage
- Unsuccessful surgical outcome